The Nigerian banking landscape is gradually shifting from conventional to digital banking—a transformation catalysed significantly by technological advancements. The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is serving as a catalyst, disrupting the established norms within the traditional banking sphere. This disruption is loosening the longstanding ties that have bound traditional financial institutions’ various elements together, paving the way for fresh innovations and novel operational paradigms.
The integration of AI into banking holds the potential to enhance traditional financial services across multiple dimensions. Often, repetitive tasks at the front office can be automated through AI, leading to increased efficiency. Additionally, AI can streamline the process of addressing customer inquiries, resulting in more effective interactions. Furthermore, leveraging AI in the banking and financial sector offers the prospect of reducing operational expenses, heightening the overall efficiency of financial establishments, and eradicating mundane daily tasks. This, in turn, expedites the cycle of innovation.
An extensive survey conducted by The Economist Intelligence Unit underscores the significance of AI. A staggering 77% of banking professionals believe that the ability to harness the potential of AI will be the determining factor between triumph and failure for financial institutions. Projections suggest that by 2030, the incorporation of AI into financial services could yield savings exceeding $1 trillion. Notably, traditional banks are anticipated to curtail around 22% of their total costs through the adoption of AI (Marsh & McLennan, 2019).
Integrating AI in banking and financial services yields multiple benefits, such as cost reduction, fraud reduction, heightened efficiency, and the eradication of routine tasks, culminating in an environment conducive to rapid innovation. For instance, the Economist Intelligence Unit Survey reveals that banks predominantly employ AI in fraud detection (58% extensively and an additional 32% to some extent) and optimising IT operations (54% extensively and 36% to some extent). Nearly all banks presently utilise AI to varying degrees or have plans to do so within the next three years, spanning various business domains from operations to customer experience. Anticipated areas for substantial growth include personalised investments (17% planning adoption in the next 1-3 years), credit scoring (15%), and portfolio optimisation (13%).
In Nigeria, businesses are keenly tapping into the potential of cutting-edge technologies to drive their growth strategies. According to Equinix’s 2023 Global Tech Trends Survey, 47% of Nigerian businesses actively embrace interconnection, and over 90% are banking on artificial intelligence (AI) benefits to expand their operations, enhance efficiency, and stay competitive in the digital era. Moreover, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly curbed banking fraud, particularly in the face of rising credit card fraud due to the expansion of e-commerce and online transactions. AI-driven fraud detection systems meticulously analyse customer behaviour, location, and spending patterns. These systems promptly activate security protocols upon detecting anomalies. The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners noted that in 2019, 13% of businesses integrated AI into their fraud prevention strategies, with an additional 25% planning to adopt AI by 2020.
Furthermore, using AI chatbots extends to offering personalised financial product recommendations to customers through AI-driven data analysis. These triggers targeted marketing of the bank’s products and bolster sales improvement, according to PIOTECH. In the UAE, a pioneering virtual assistant named “EVA” has emerged as the inaugural digital aide in the Middle East and North Africa region. EVA possesses the remarkable ability to comprehend both Arabic and English languages, engaging users in natural conversations. Similarly, Kuwait has introduced “Banky,” an AI-based virtual assistant that ensures secure, dependable, and swift interactions while addressing customer inquiries about banking services and products. In Egypt, the advent of “Zaki” has been announced, an intelligent virtual assistant heralded for enabling clients to stay informed about the latest decisions from the Central Bank of Egypt and effortlessly explore diverse offerings across various banks.
Drivers of AI Disruption in the Banking Industry
1. Emergence of Big Data: The surge in big data has profoundly impacted the banking industry. Customers now digitally engage with banks, generating structured (transactional) and unstructured (messages, images, videos) data. Banks leverage this data to offer highly personalised services, using a 360-degree view of customer interactions, including personal info, transactions, and social media.
2. Infrastructure Accessibility (Swift computers, hardware, software, Cloud): The rapid growth of cloud technology, coupled with robust computational resources and infrastructure, enables swift and cost-effective processing of vast datasets. This enhanced scalability empowers organisations to embrace AI with greater readiness than before.
3. Regulatory Demands: Banks face stringent regulatory oversight, necessitating accurate and timely reporting to fulfil obligations. Compliance involves gathering data from diverse sources. AI-powered solutions offer the potential to tackle present financial challenges by automating data collection, expediting decisions, and strengthening regulatory preparedness. As AI advances, it will reshape front and back-office operations, prompting adjustments to regulations and global financial structures. This transition allows compliance teams to adopt new tech for enhanced future readiness strategically.
4. Competition: In an ever-competitive landscape, banks are in perpetual rivalry with industry counterparts and, increasingly, FinTech companies. The quest for superior client services has made technology a pivotal distinguishing factor. Enterprises now capitalise on cutting-edge technologies to tap into their extensive data repositories. Consequently, AI has emerged as the tool of choice for banks to enhance existing services, introduce novel offerings, and deliver highly personalised customer experiences.
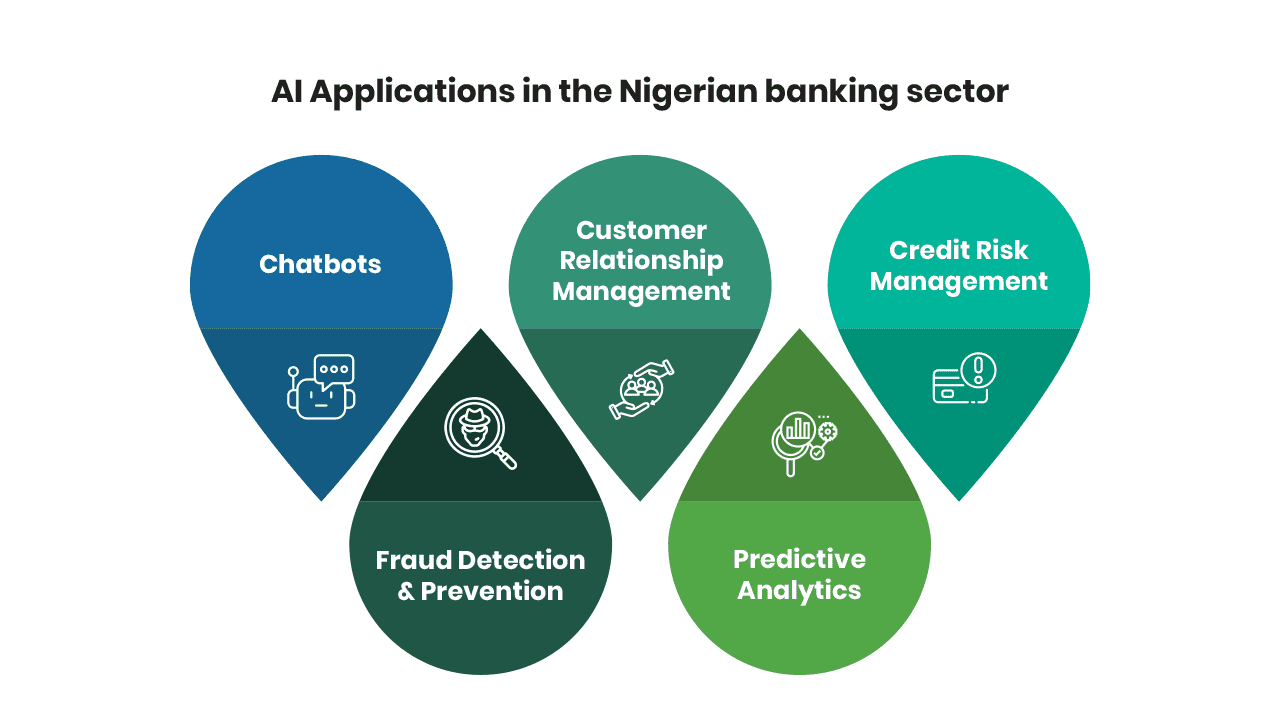
AI Applications in the Nigerian banking sector
The utilisation of disruptive AI technology is transforming various aspects of banking services in Nigeria. The following outlines key areas where AI has made significant contributions within the banking industry:
1. Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots, equipped with Natural Language Processing (NLP), engage customers around the clock, enriching online interactions. Beyond addressing routine inquiries, these chatbots facilitate new account openings and proper routing of complaints to relevant customer service units. In Nigeria, seven (7) Deposit Money Banks (DMBs) have actively embraced the digital economy trend by incorporating Artificial Intelligence-powered chatbots into their services. These banks, including Zenith Bank (Ziva), Fidelity Bank (Ivy), First City Monument Bank (Temi), UBA Group (Leo), Access Bank (Tamada), Heritage Bank (octopus chatbot), and Keystone Bank (oxygen chatbot), are not only competing in the adoption of AI chatbots but also focusing on performance efficiency and customer satisfaction. These chatbots enable users to conduct banking transactions seamlessly and enhance the customer experience.
2. Fraud Detection & Prevention: AI-powered solutions are enhancing fraud detection and risk management in Nigerian financial institutions, ensuring customer protection and overall stability. A recent report on Fraud and Forgeries within the Nigerian Banking System shows that fraudulent incidents within Nigeria led to a loss of N472 million in Q’1 2023. In response, the Central Bank of Nigeria mandates robust risk management systems for all financial institutions. AI’s rising role in credit risk management and fraud detection, particularly in fintech and digital banking, improves credit evaluations by forecasting default likelihood.
3. Customer Relationship Management: AI empowers Nigerian financial institutions to offer customised services catering to individual customer needs, elevating customer experiences and satisfaction. Customer relationship management holds immense significance for banks. Personalised 24/7 services such as facial recognition and voice commands for financial app logins are offered to individual customers. AI-powered analysis of customer behaviours aids in automated segmentation for targeted marketing, fostering improved customer experiences and interactions.
4. Predictive Analytics: The advent of Machine Learning (ML) and AI enables precise forecasting. Data Analytics and AI are applied to revenue forecasting, stock price predictions, risk monitoring, and case management. Growing data availability enhances model performance, reducing the need for extensive human intervention. For instance, Nigerian banks such as UBA and Access Bank invest in predictive analytics by leveraging advanced data analysis techniques to forecast future trends and customers’ behaviour.
5. Credit Risk Management: Regulatory focus on risk supervision compels financial institutions in Nigeria to develop robust models. AI finds prominence in credit risk management, particularly in the Fintech and Digital Banking sectors. AI assesses borrower creditworthiness by leveraging data to predict default probabilities, enhancing decision accuracy. This shift to insight-driven lending replaces expert judgment, optimising customer acceptance and minimising credit losses for financial institutions.
How Nigerian banks can transform to become AI-induced.
A comprehensive approach is vital to facilitate Nigerian banks’ transformation into AI-induced entities. This involves strategies encompassing customer engagement, AI-driven decision-making, core technology and data infrastructure enhancement, and transitioning to a platform operating model.
Approach 1: Reimagining Customer Engagement
- Empowering Personalised Solutions: Shift from standardised products to customised solutions, integrating customer preferences and automated decision-making to extend value propositions beyond basics.
- Seamless Integration with Partner Ecosystems: Embed banking services within existing platforms, leveraging partner data for natural customer engagement.
- Revamping Omnichannel Experiences: Enable smooth transitions across communication channels, maintaining a unified view of customer interactions inspired by successful internet companies.
Approach 2: Building AI-powered Decision-making.
- Establishing an AI-Powered Decision Layer: Develop a scalable AI-driven layer to replace or enhance human judgment, deploying advanced analytics models across various business areas.
- Enabling Scalable Model Development: Create repeatable processes, foster team collaboration, and incorporate AI into regular business processes.
- Facilitating Continuous Improvement: Establish feedback loops, integrate evolving AI capabilities, and enable rapid integration of emerging technologies.
Approach 3: Strengthening Core Technology and Data Infrastructure
- Developing a Robust Core Technology Framework: Build a scalable core-tech foundation aligned with the bank’s AI-first vision and supporting unified tech-forward strategies.
- Effective Data Management for AI Integration: Ensure data liquidity, break down silos, and enhance data security and privacy.
- Modern API Architecture: Implement APIs for controlled access, reducing silos, promoting flexibility, and enhancing customer experiences.
Approach 4: Transitioning to Platform Operating Model
- Revolutionising the Organisation’s Operating Model: Embrace a platform operating model for agility, breaking functional silos, and fostering collaboration.
- Platform Operating Model Essentials: Utilise cross-functional platform teams managing assets and budgets and delivering products/services to customers.
- Breaking Silos and Boosting Agility: Align goals across integrated business and tech platforms, accelerating responsiveness and effectiveness.
- Achieving AI-First Transformation: Transform all layers of the capability stack, align AI goals with strategic objectives, assess the current position, and create a comprehensive transformation roadmap involving business, tech, and analytics units.
Conclusion
The Nigerian banking sector is transforming from traditional to digital banking, primarily driven by the disruptive impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI). This evolution is marked by increased efficiency, cost reduction, and innovative operational paradigms. AI applications like chatbots, fraud detection, and predictive analytics are reshaping the industry. Nigerian businesses are actively embracing AI, particularly for growth and operational efficiency. To become AI-induced entities, Nigerian banks must adopt a comprehensive strategy encompassing personalised customer engagement, AI-powered decision-making, robust technology infrastructure, and a transition to a platform operating model. This strategic approach positions them for future competitiveness and continuous innovation in the digital era.
Written by:
Temitope Abimbola
Research Associate