Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. –NIST (September 2011).
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are compelled to embrace cloud technology to drive innovation, enhance business agility, optimise operational processes, and reduce costs. Cloud Computing will help companies stand the test of time in the long run, propelling them to maintain and improve the growth structure of their organisation. In Africa today, more and more companies are using the cloud as the core piece in building a holistic digital transformation organisation structure. Despite Nigeria’s challenges, industries like finance, business, and oil sectors have started deploying cloud computing services in their systems and are thriving.
Defining Cloud Computing: A Paradigm Shift in Technology
Cloud computing was inspired by using cloud-shaped symbols seen in flowcharts and diagrams to depict the Internet. (Techtarget, Nov 2022). Throughout the years, cloud experts have varying definitions of cloud computing. However, one explanation stood out; although it still needs to be universally accepted, it is currently the most common definition. This definition is the National Institute for Science and Technology (NIST) definition, which states that Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This definition was championed by Peter Mell and Timothy Grance in a special publication by NIST in September 2011.
Cloud Computing Services: A Multifaceted Landscape
Services in cloud computing nowadays cover a wide range of options like storage, artificial intelligence, natural language processing, networking, processing power, etc. Any service you can think of that doesn’t necessarily need you to be close to computer hardware can be delivered through the cloud. Most large companies consume cloud services to implement their services; for example, Netflix relies on the cloud to run its business systems and video streaming services. Another example is Gmail, which offers a wide range of services through cloud computing, from consumers backing up photos on their smartphones to allowing large companies to host and run their applications on their platforms using the cloud. Even if there are disadvantages to using cloud computing services in different companies, like the new risks and cost of implementing the service with their business processes, the advantages outweigh the downsides as more and more software vendors are rapidly hosting their applications on the Internet rather than standalone servers by subscribing for only the amount of storage needed to run their applications.
Charting the Future: Cloud Computing’s Role in Digital Transformation
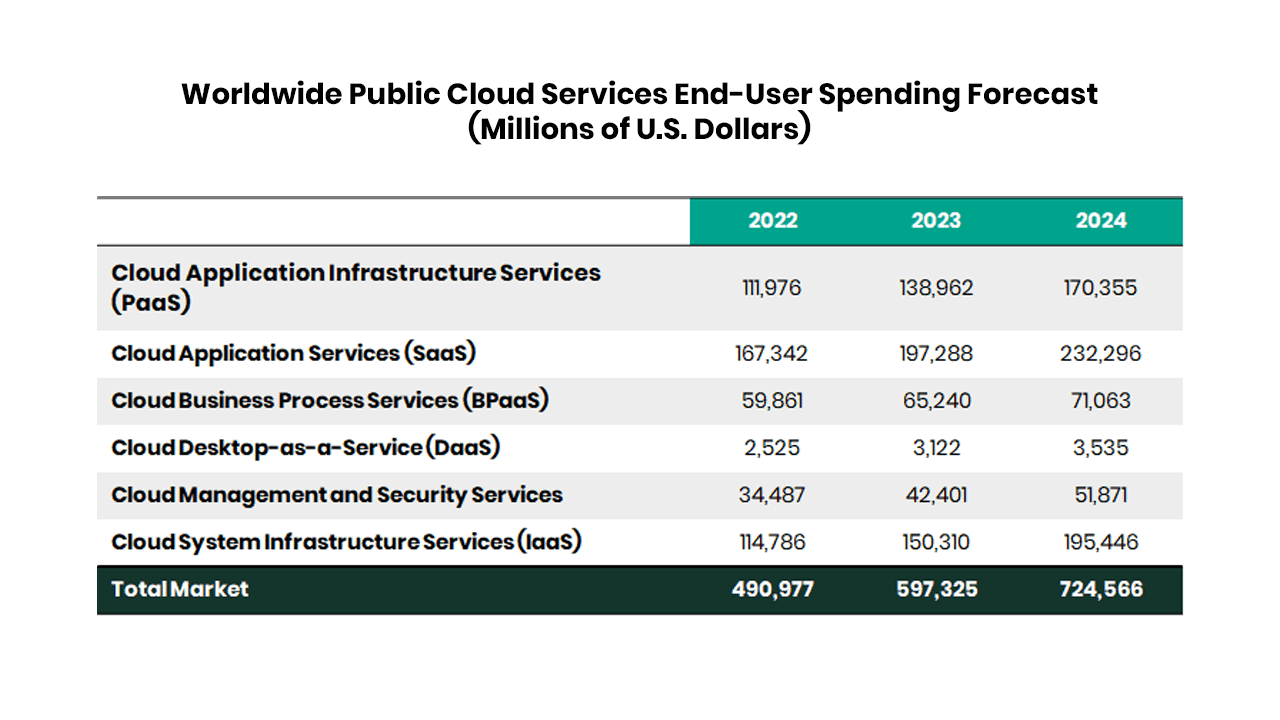
Cloud computing drives the next phase of digital business transformation as organisations pursue disruption via emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence and the metaverse. Gartner Inc. forecasts that global spending on cloud computing services is expected to grow from $491 billion in 2022 to $597.3 billion in 2023, thereby making a 21.7% increase from the spending on public cloud services. Sid Nag, Vice President Analyst at Gartner, said, “Most organisations today see cloud as a highly strategic platform for digital transformation, which requires hyper-scale cloud providers to offer more sophisticated capabilities as the competition for digital services heats up.” All the elements in cloud computing services are forecasted to grow at the end of 2023. Especially Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), which is expected to experience the highest end-user spending growth in 2023 at 30.9%, followed by platform-as-a-service (PaaS) at 24.1%
(see Table 1, which shows Worldwide Public Cloud Services End-User Spending Forecast (Millions of U.S. Dollars)).
BPaaS = business process as a service; IaaS = infrastructure as a service; PaaS = platform as a service; SaaS = software as a service
Note: Totals may not add up due to rounding.
Source: Gartner (April 2023)
Also, Gartner predicts that by 2026, 75% of businesses will adopt a digital transformation model predicated on clouds as the fundamental underlying platform.
Core Elements in Cloud Computing
Software as a Service (SaaS): This version of cloud computing is what people are primarily used to on a day-to-day basis, as it is simply the delivery of applications as a service. The capability is provided to the consumer on a per-seat or per-user basis, as the consumer does not need to worry about managing or controlling the cloud infrastructure or individual capabilities. This can be accessed through an application or a web browser. Examples of SaaS include CRM such as Salesforce and Microsoft’s Office 365.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): This allows the ability to deploy cloud, custom-created, or acquired applications using programming languages, frameworks, and tools available in the cloud platform. Here, the user is not concerned about managing and controlling the various cloud infrastructure like servers, operating systems, networks, storage, etc.; it is usually used on a pay-per-use or charge-per-use basis. PaaS is used when there are a lot of programmers or software developers working similarly on a particular project, and this helps make the process of creating/deploying applications simple, including database management, development tools, middleware, etc. Examples include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, and Heroku.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This provision is for consumers who want to build applications from scratch and have the technical capabilities in their companies to control and manage most of the elements themselves, like storage, operating systems, and deployed applications. This provision could be hired as it refers to the most vital building block of computing, which includes physical or virtual servers, storage, and networking. Examples include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Compute Engine.
The Imperative of Cloud Computing for Nigerian Businesses
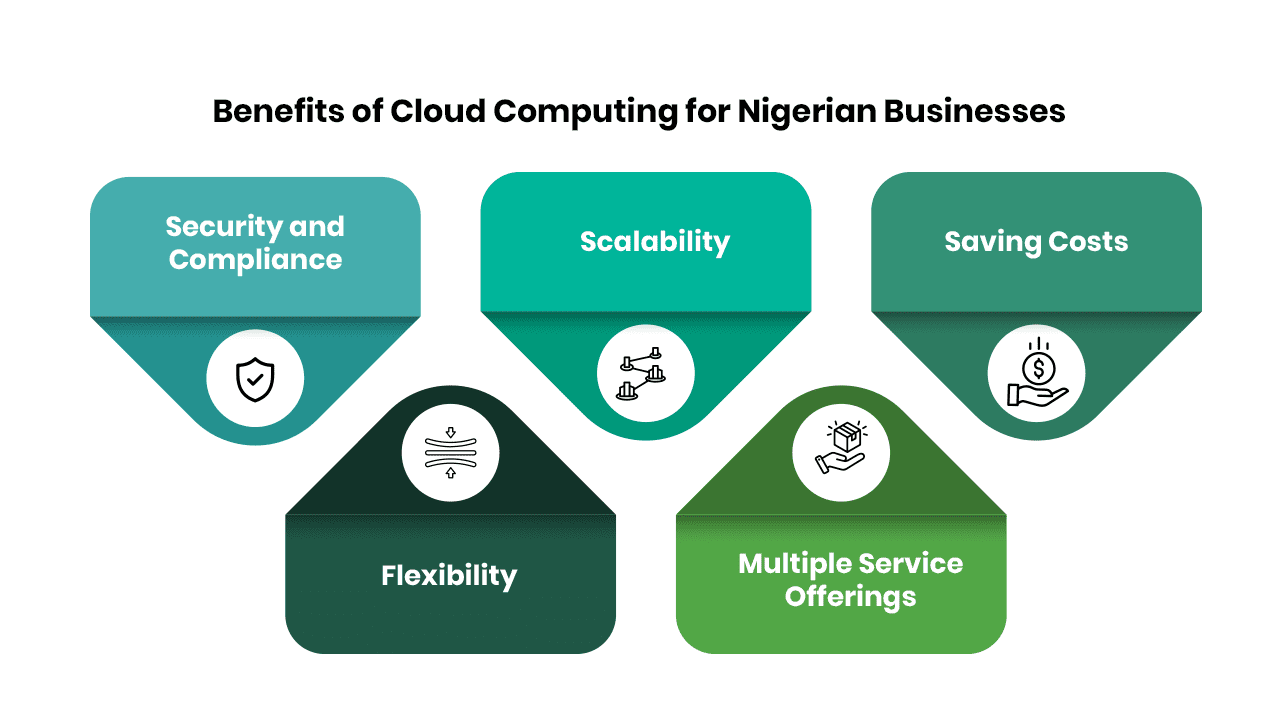
With large companies globally investing in the cloud and spending vast amounts of money, as seen in Table 1 above, it has never been more essential for businesses in Nigeria to migrate to cloud services. Before the emergence of cloud computing, big and small businesses stored their data in servers and hard drives, which could be more scalable at speed. These servers and hard drives crash frequently from the amount of data subjected to, causing many problems for the business. Using cloud computing in Nigerian businesses today can push organisations through in times of crisis, leading to many benefits. Some of these benefits include:
Security and Compliance: Cloud computing Service providers always build their services with security services that will help businesses protect their data during a crisis. With a cloud structure IT infrastructure, it helps to back up data so that whenever there is a disaster within a company, it will help the company recover to its full functionality. Security is vital in the cloud computing world as it ensures the privacy of companies’ data, making most organisations today opt for private cloud databases. Compliance and security in cloud computing control access and protect privacy by ensuring data is secured using data and user authentication. In this way, companies can maintain their cyber security to a creditable extent and provide the privacy of their company’s infrastructure.
Scalability: Scalability is an essential procedure in cloud computing. With the ever-demanding changes happening in the business world today, cloud computing will constantly adapt to meet these changes to help a business scale and weather the storm. Developers in cloud computing are gaining more popularity by expanding IT infrastructure with the help of the cloud’s numerous IT resources to meet these changes in computing and development.
Saving Costs: With no need to purchase hardware or software for cloud computing, the organisation has many benefits to save costs. Capital costs like computing, storage, and networking will be reduced drastically, as well as reducing operational costs, upgrade expenses, and maintenance.
Flexibility: With the help of cloud computing, most companies and organisations transitioned into the remote working structure. Employees can now work from anywhere, provided they can access data to work. This has created much flexibility for numerous employees, saving them time and effort in carrying out their other responsibilities and eliminating the need to spend long hours commuting to work.
Multiple Service Offerings: Cloud computing has a plethora of service providers who have been aiding organisations with their cloud computing needs and stating the need for cloud computing in today’s businesses to thrive and develop. Using one of these service providers to migrate into cloud space is vital as it poses many benefits to the company and individual at large. Numerous cloud service providers, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud Services, and Adobe Creative Cloud, offer diverse solutions to back up data and resources, ensuring the preservation of IT infrastructure.
In conclusion, the importance of clouds in today’s business can never be over-emphasised. The gap in the performance of Nigerian companies that have been more strategic in their methods in adopting cloud computing technology to the laggards is vast. Companies that have invested in cloud technology as part of their digital transformation process have gained about two times the average profit growth of companies slow to implement and use cloud services. However, it is not too late to start now. The business world is always overwhelming with its uncertainty and doubt. Now is the time for organisations that have not fully embraced cloud technology to do so and to build and expand their capabilities. Cloud technology’s flexibility and agility will enhance business processes and ways of working and doing business.
Written by:

Ogonna Okorie
Senior Analyst