Today’s hyper-competitive and chaotic economic situation makes us believe that being able to predict the future 12–18 months in advance is not as important as we thought. Instead, being able to adapt to the changing expectations of the economy and customers’ value quickly is more critical. Those enterprises who can tweak and adjust their business models rapidly have a better opportunity to grab market share and maintain a competitive edge.
“If you went to bed last night as an industrial company, you’re going to wake up today as a software and analytics company.” This statement was made by GE’s then CEO back in 2014. The underlying message of his statement is that unless you invest in software, you will not remain competitive and so you may never wake up.
Therefore, if you are not the first or fastest, your competitor may win. Almost every enterprise uses software and analytics tools to assist with quick decision making and improve productivity. Especially for software-as-a-service companies, it’s vital to stay ahead of the competition. One possible way to provide better, faster and more reliable services is with the use of microservices.
A microservice is a software application with a very small footprint. It uses only the memory and the processing power that it requires to perform a function. Microservices are used to perform a singular function. With microservices, you can decentralize your entire application and decouple it into services that act as separate entities.
For instance, we can have a sales service or an HR service. All these different services combined will create a business solution. A microservice in itself is a complete application, but when you combine all of these microservices, you end up with a business solution.
How Microservices Reposition Organisations
Many organisations have strong brands, solid reputations, valuable experiences, and extensive customer bases. However, if we look inside these organisations, we can see that they struggle to adapt to change. They are accustomed to taking their time to develop, launch and exploit their products or services. In this new era, time must be used judiciously. With microservices, organisations can be repositioned in terms of scalability, tolerance, cost, resource and many more.
Microservices Present Scalability to Organisation
With microservice scalability, organisations can add services or remove services as the need requires. For instance, in the western world during the December holidays, there is a lot of retail activity. It is possible to add services during this period. Once the activity has sort of scaled down, it is now possible to remove those services. So, we can scale our services depending on the needs of the business. Also, if a business intelligence dashboard is no longer meeting your needs, you can swap it out for another more suitable option without breaking the whole system.
Microservices Present Tolerance to Organisation
In terms of tolerance, what happens is that if one of the microservices go down – let’s say something happens to it – then we can simply remove that microservice from the entire system, fix it, and then redeploy it back again. So, in other words, while some maintenance is taking place on one microservice, the rest of the system continues to operate like normal. There is no downtime with this system.
Microservice Reduce Organisation IT Cost
Organisations can save money and have greater customer loyalty if they adopt Microservices.
Microservices reduce costs in the following ways:
Agility: Microservices architecture speeds up deployment and shows that processes can be accomplished in shorter times. Shorter times to deployment cut what IT spends.
Efficiency: reducing the amount of complexity required to run a given application also results in savings. Up to 50% of costs may be saved by reducing the complexity of an application’s infrastructure.
Flexibility: Dispersing functionality across multiple services eliminates an application’s susceptibility to a single point of failure (SPOF). Stronger applications perform better, have fewer outages, and have the potential to scale rapidly.
Accountability: Decreased downtime directly increases revenue by improving user engagement, increasing consistency, and sharpening efficiencies. All these byproducts lead to increased user retention and engagement.
Microservices Reduce Organisation Resource
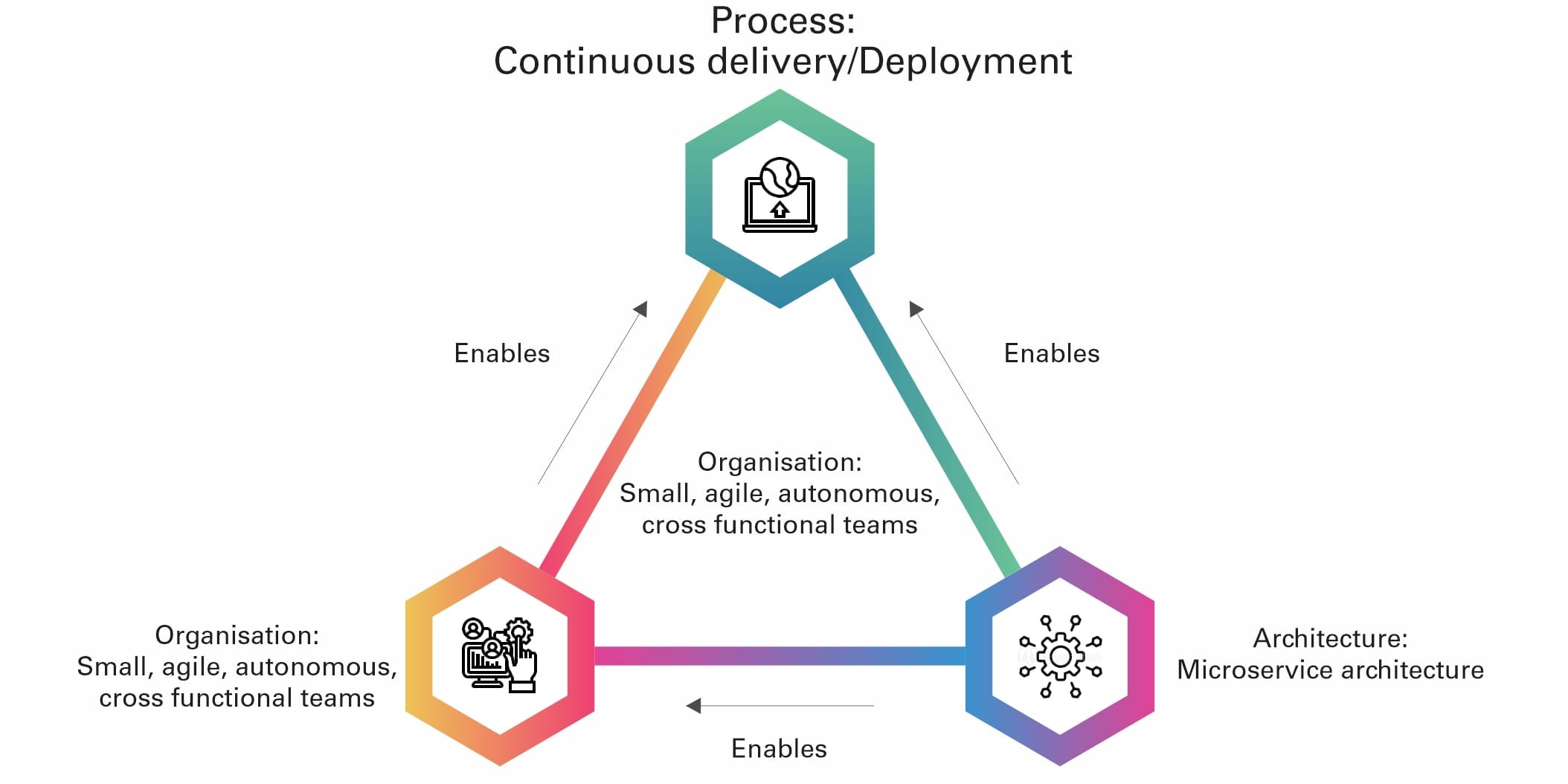
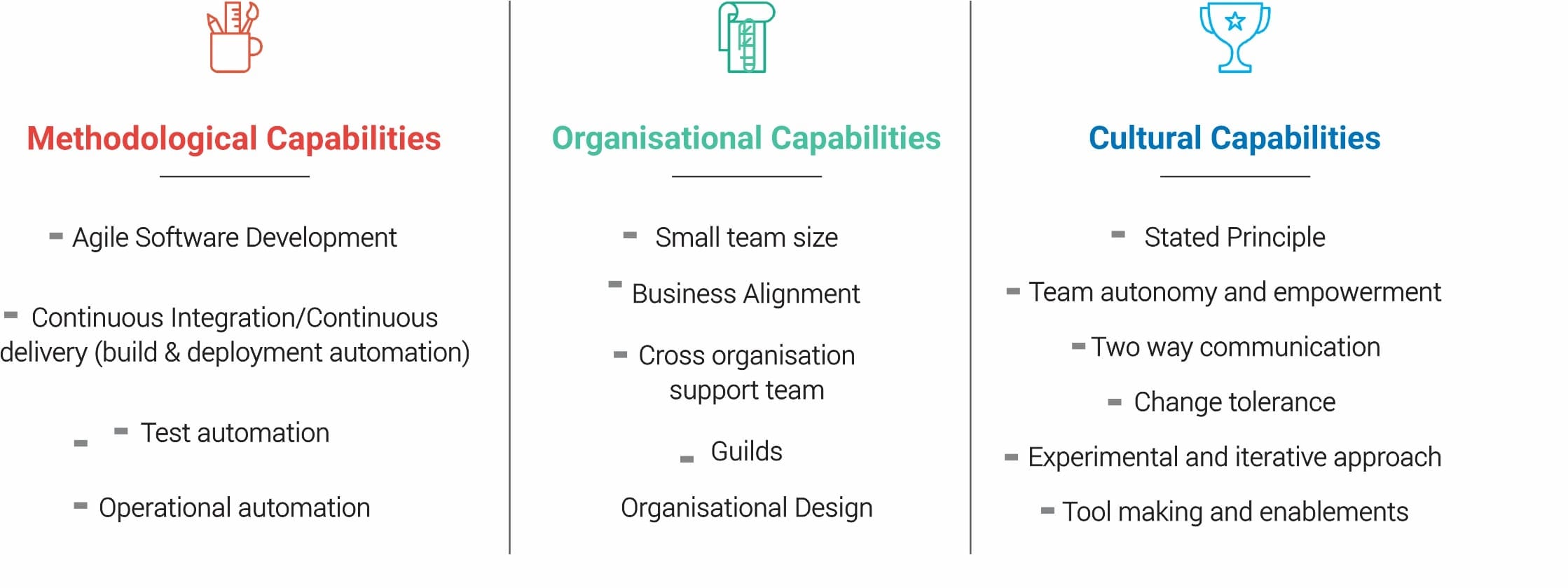
The goal of microservice architecture is to accelerate software development by enabling continuous delivery and deployment.
The microservice architecture does this in two ways:
- Simplifies testing and enables components to be deployed independently
- Structures the engineering organisation as a collection of small (6-10 members), autonomous teams, each of which is responsible for one or more services
These benefits can only be achieved by the careful functional decomposition of the application into services. A service must be small enough to be developed by a small team and to be easily tested
Lastly, Enterprises that adopt microservices are in an excellent position to take advantage of these changes that are coming.
Written by:

Ibrahim Asunmoh
Consultant