“The changes are so profound that, from the perspective of human history, there has never been a time of greater promise or potential peril.” – Klaus Schwab, Founder and Executive Chairman of the World Economic Forum.
We are currently witnessing the new dawn of a universal technology revolution which is known as the” Fourth industrial revolution”.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0 is the reformation of the traditional and industrial manufacturing practices involved with the latest technology. It is mainly used in Internet of Things (IoT) deployments and large-scale machine to machine communication (M2M) to enhance communication, increase automation, as well as diagnosing and analysing smart machines without human monitoring or involvement.
According to Klaus Schwab, the Fourth Industrial Revolution is building on the Third, Digital Revolution, bringing a “fusion of technologies that is blurring the lines between the physical, digital, and biological spheres.”
Digital technologies have started coming forward and is implemented in organisations most especially financial institutions in Nigeria. Examples are Internet of Things (IoT) systems are , Location detection technologies, Mobile devices, Authentication and fraud detection, Smart sensors, advanced processes, Big analytics, 3D printing, customer profiling, Multilevel customer interaction and Data visualisation.
Now, let us talk about Fintech.
Fintech is the abbreviated word for “Financial Technology”. Fintech consists of new technology applications, processes, products, or business models in the financial services industry, made up of one or more complementary financial services and provided as an end-to-end process via the internet. Fintech is also considered as “any innovative idea that improves financial service processes by proposing technology solutions according to different business needs, while the ideas could also lead to new business models or even new businesses.”
Simply put, Fintech is any technology that helps to automate and improve the way financial transactions and processes are carried out. The emergence of this industry makes use of technology to enhance activities in finance.
The origination of Fintech came from industry 4.0, i.e. Fintech comprises of the technologies that came in industry 4.0. Some of these technologies include artificial intelligence (AI), big data, robotic process automation (RPA), and blockchain.
In most financial institutions in Nigeria, financial technology is used to automate insurance, investments, risk management, trading, and banking services. These technologies are used to run their business processes because of their creativity, innovation, and unique and cutting-edge work styles and culture, giving them an edge over traditional banking. It explains why Fintech is seen as the future of the financial industry in Nigeria today.
Fintech made $554 million of venture capital funding last year from January down to September as opposed to the $487 million capital funding made in 2014. In 2016, London fixed itself as a central location of Fintech, which has proved itself the latest technology to look out for. London being the hub of Fintech in Europe, has witnessed this technology benefit as 53% of the investment is put into Europe’s financial technology market.
More than 70% of stock trading decisions in the United States of America are carried out based on computer algorithms, as opposed to individual experts making 10% of the stock trading decisions.
The shows that the amount spent on financial consulting services have been reduced.
In Bangladesh, micro-loans powered by technology has revealed a new rave of financial empowerment to the less advantaged people in the rural areas.
Now, let’s look into some industry 4.0 technologies that are the growing trend in Fintech in Nigeria.
Blockchain
Blockchain was developed purposely for finance and has ties to financial institutions. In Nigeria today, blockchain applications are one of the technologies that are revolutionising financial institutions. Ranging from bonds where applications self-execute themselves and allow bondholders to be paid automatically immediately the agreement terms are met to Cryptocurrency (digital/electronic coins used for transactions), where blockchain helps keep track of records, removing any hackers or fraudsters by storing valuable information about money availability, sender /receiver’s reputability and the legitimacy of the transaction process thereby ensuring you have a safe and fast transaction. Blockchain is essential for financial institutions because it ensures more secure activities like independent and smart verification of their clients, secure payment processing and an automated trading process. Thus, ensuring a massive reduction in fraudulent activities all over.
Fintech is at the core of the financial service industry, with blockchain in charge of big data and disruption (Iskandar, 2017). In 2015, World Economic Forum estimated that by 2025, 10% of GDP would be stored on blockchains or blockchain-related technology. Blockchain is regarded as the future of banking globally, and it is said to have restructured the fintech system like the internet did to the media years ago (Ito et al., 2017).
A survey carried out by McKinsey in May 2016 on global banking executives deduced that a substantial amount of the executives thought that blockchain would have a huge impact on the Fintech sector within three years, while some of them believed that the impact would take place in 18 months.
Big Data and Analytics
The banking industry depends on data to operate and, as such, generates tons of data in a day. Banks can use Big Data to improve their operations and develop segmented marketing strategies. It provides the ability for financial institutions to utilise and analyse data to make profit. Analysing data opens a whole wealth of ideas, given that it represents the ability, performance, or information of a bank at a time. By knowing how to analyse data, a bank/financial institution has a huge advantage over its competitor because it will be able to predict and adapt to the evolving trends and customer demands, thereby quickly providing satisfaction to the customer. Nowadays, a large volume of information is collected rapidly using fintech technologies, unlike before when data collection could run into weeks or months. With data analytics, a large volume of data can be extracted and used for better analysis, insights, and foresight, thereby making it possible for organisations to devise possible future scenarios and predict customer behaviour and make the right decisions to make profit.
The biggest bank in Denmark is known as the Danske Bank. It has a customer base of more than 5,000,000 and is having a hard time with its fraud detection methods, in which the fraud detection method has 40% of accurate fraud detection, allowing it to manage a total of 1200 false positives every day.
Danske Bank knew that they had to do something immediately to correct this and decided to partner with a company called Teradata, a renowned analytics and database service provider, to check out their fraud detection techniques. They soon discovered some tangible results, and Danske Bank observed false positives reduced to 60% and was estimated to reduce further to 80%, thereby achieving a 50% increase in true positives. This made them have a considerable rise in operating profit of $70 million in 2018.
This shows how Data analytics restored life to the laid-back Danske Bank. Data analytics have gone ahead in causing a huge disruption in many industries today, especially the Fintech industry and has been very successful in its growth and development (Hassani et al., 2018).
With FinTech, financial institutions can now collect and manage big data to get a holistic view of each of their customers. For example, using data analytics, a bank can predict whether a customer will be able to pay up a loan. By using information such as utility bills, credit history, census data together with predictive machine learning, the result can be gotten in an instant. However, looking back 20 to 30 years ago, it takes a group of employees’ time and effort to determine your credit score.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Today, the Fintech industry is undergoing an evolution caused by economic instability and the COVID-19 pandemic, making banks look for ways to cut down cost and improve revenue. Many banks have adopted Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to address this growing need, and as such RPA is a major factor in driving digital transformation into their banking processes. As per Forrester’s RPA trend and forecast, it is estimated that this year the market for knowledge-work processes robots will reach $2.9 billion. According to Gardner, by the year 2022 the market size for RPA is projected to reach $2.4 billion. Furthermore, Fortune Business Insights published a report recently saying that RPA market size is estimated to reach USD 6.81 billion come 2026.
In the financial industry, RPA is the process of assigning repetitive, manual tasks to robotics instead of humans to streamline processes. This costs way less than the traditional banking method because fewer employees are needed as the process is automated. Most banks in Nigeria now implement RPA to perform manual processes that often are repetitive and completed daily, such as verification, risk assessments, customer onboarding, compliance processes, security checks, data analysis, and other repetitive administrative activities. This will increase staff accuracy and efficiency, promoting excellent business outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence
In the financial industry, AI is used in very different forms. It is used for algorithms that can predict changes in the stock market and give insight into the economy, provide insights on customer spending habits and allow financial institutions to understand their clients better. You can go ahead to say that AI is the most used technology in Fintech, offering the potential to play an even bigger role in the finance industry as developments continue.
As per Autonomous Research’s prediction, by 2030, AI technologies will enable Financial Institutions to lower their operational costs by 22%.
In Fintech, creditors make use of AI, i.e. Credit scorer, to determine whether to lend individuals money. The chatbox is also a booming trend in the Fintech industry, using language processing and speech generation to provide round-the-clock service, quick response to inquiries and complaint resolution. According to business insider report, AI application’s cost savings for banks is expected to be at $447 billion come 2023. This is one AI tool that customers have come to depend on because it provides a smooth process when banking individually.
Cloud Computing
According to Forbes, cloud computing was estimated to rise from $67B to $172B in 2015 to 2020, thereby having a 19% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). Moreover, at the end of 2025, the global fintech market size is expected to rise from $124.3 billion USD and have a CAGR of 23.84%.
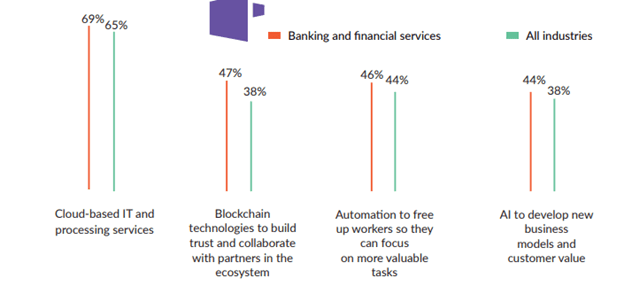
Cloud computing is an emerging technology in Fintech, with 22% of fintech applications running on the cloud.
There are enormous benefits that come with the package of cloud technology. It can help the financial sector store large amounts of data in the cloud by providing unlimited storage without fretting about data. Purchase of servers, data centres, related IT infrastructure, and cost of maintenance by the financial industry can be optimised greatly. Cloud computing has scalability capabilities that the financial industry can use to scale up resources so that tasks are performed smoothly without any problem, most especially when there is a need for Fintech to introduce new policy regulation.
The Fourth industrial revolution has really emerged in our economy, especially in the Fintech industry. Industries and businesses are being impacted positively, and in the future, industries, especially the Fintech industry, will leverage on the power of industry 4.0. In 2019, the industry 4.0 market was said to be valued at USD 71.7 billion and in 2024 is estimated to rise to USD 156.6 billion. This means that industry 4.0 has a CAGR of 16.9% from 2019 to 2024. Banking, mortgage, insurance, stocks, forex and other fintech sectors succeed in the digital and financial process automation space in Nigeria due to the positive influence of industry 4.0 technology.
Written by:

Ogonna Okorie
Senior Analyst
References
Wikipedia: Industry 4.0
Wikipedia: Financial Technology.
Fintech Weekly Magazine: Major FinTech Trends for Financial Industry In 2020
Fintech Weekly Magazine: How blockchain applications can transforming society
Cloud Computing in the Financial Industry
Nigeria’s competitiveness and fourth industrial revolution
Banking and Financial Services-Business 4.0-TCS
FinTech in 2021: Top predictions and trends
Statistics
[9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18]