The business landscape constantly evolves because of technological advancements, societal shifts, and global interconnectedness. For organisations to thrive and remain relevant, they must continuously innovate and embrace agility and adaptability to meet global demands.
Skills transformation has become a crucial and strategic initiative for organisations. Not only does it enable businesses to thrive in a rapidly changing landscape, but it also empowers employees to navigate their careers successfully and remain relevant. Investing in skills transformation ensures that organisations have a skilled workforce that can effectively respond to industry disruptions, drive innovation, and adapt to new technologies, processes, and evolving business needs.
The World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Future of Jobs Report 2020 indicates that 40% of employees will require six months or less reskilling by 2025. The WEF report highlights the need for organisations to prioritise skills transformation and prepare their Talents for the future of work.
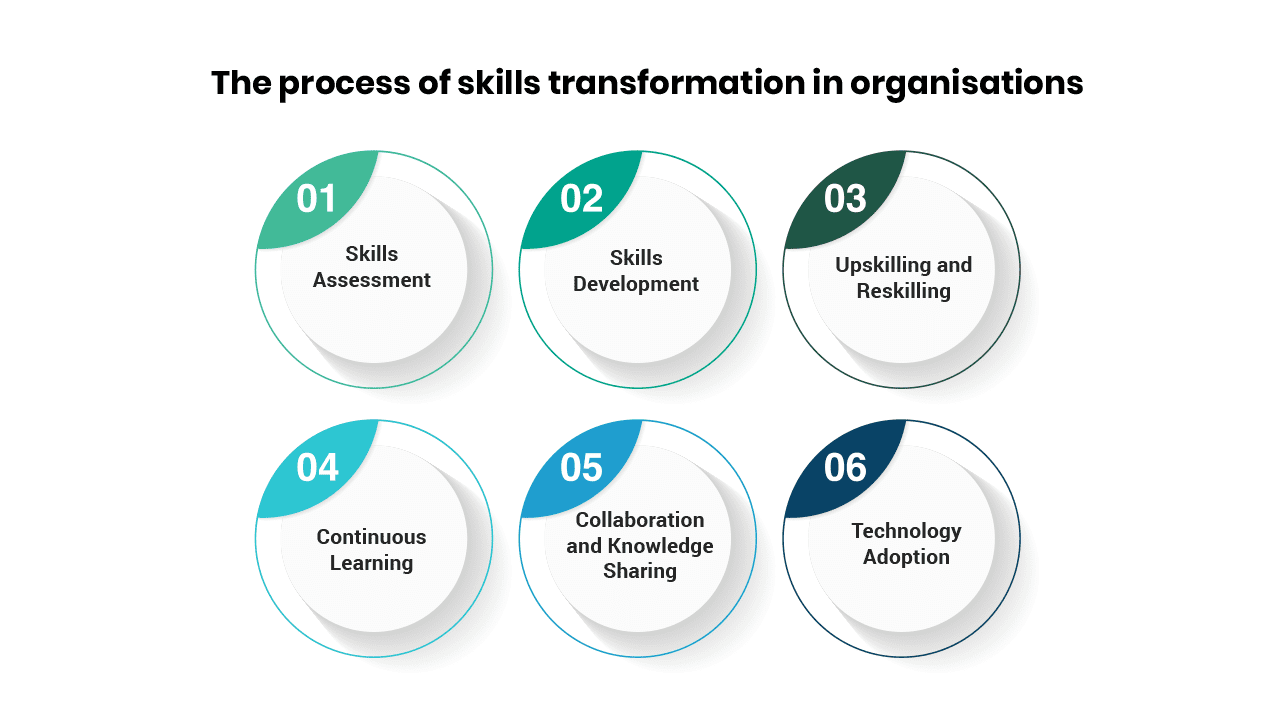
The process of skills transformation in organisations typically involves the following elements: Skills Assessment, Identify Skill Gaps, Learning Programs, Training & Upskilling, Practical Application, and Continuous Learning.
1. Skills Assessment: Identifying the existing skills within the workforce and assessing their relevance and alignment with current and future organisational needs. This assessment involves evaluating individual capabilities, conducting a skills gap analysis, and identifying areas for improvement.
2. Skills Development: Implementing learning and development programs to address identified skills gaps and provide employees with opportunities to acquire new skills. The implementation may involve training sessions, workshops, online courses, mentorship programs, and other learning initiatives.
3. Upskilling and Reskilling: Upskilling aims to enhance existing skills, deepen knowledge, and expand expertise in a specific area. Reskilling involves acquiring new skills different from an individual’s current skill set. Upskilling and reskilling initiatives enable employees to assume new organisational roles and responsibilities.
4. Continuous Learning: Encouraging a culture of continuous learning fosters an environment that supports ongoing skill development. It involves promoting self-directed learning, providing access to learning resources and platforms, and encouraging employees to stay updated with industry trends and advancements.
5. Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Facilitating collaboration and knowledge sharing among employees helps to foster a learning culture and growth within the organisation. Organisations can achieve this collaboration through cross-functional projects, internal communities of practice, mentorship programs, and peer learning initiatives.
6. Technology Adoption: Technology adoption involves embracing technology as an enabler of skills transformation. This adoption includes leveraging digital tools and platforms for learning (e.g., Learning experience platforms), incorporating emerging technologies into training programs, and promoting digital literacy among employees.
Why the Need for Skills Transformation in Organisations
Several factors drive skills transformation; below are some reasons why Skills Transformation has become very crucial in organisations:
1. Driving Innovation and Growth: Skills transformation fosters a culture of innovation within organisations. Organisations can drive innovation, seize new opportunities, and stay ahead of the competition by equipping employees with the skills to adopt emerging technologies, think critically, and problem-solve. The resulting effect can help drive business growth and sustainability.
2. Future-proofing the Workforce: The job market is constantly evolving, and skills in demand today may become obsolete soon. Skills transformation ensures that individuals and organisations are prepared for disruptions and changes. Individuals and organisations can develop a learning mindset and continuously acquire new skills to future-proof their workforce.
3. Employee Engagement and Retention: Investing in skills transformation demonstrates a commitment by organisations to employee growth and development. This awareness contributes to higher employee engagement and job satisfaction. Employees with opportunities for skill development are more likely to feel valued, motivated, and committed to their organisations, leading to increased employee retention.
4. Meeting Customer Expectations: Customer expectations are continually evolving, driven by technological advancements and market dynamics. Skills transformation enables organisations to align their workforce’s skills with customer needs, ensuring they can deliver solutions and services that meet or exceed customer expectations. The outcome enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
5. Adapting to Industry Disruptions: Industries are susceptible to disruptions, such as market changes, new competitors, or economic shifts. Skills transformation equips organisations with the agility and capability to adapt to such disruptions. By having a workforce that can quickly acquire new skills or pivot to different roles, organisations can navigate uncertain times and seize opportunities that arise from industry disruptions.
6. Cultivating a Learning Culture: Skills transformation fosters a culture of continuous learning within organisations. An environment that encourages the development of new skills fosters growth, curiosity, innovation, and productivity. A learning culture promotes collaboration, creativity, and exchanging ideas, leading to improved problem-solving and better organisational outcomes.
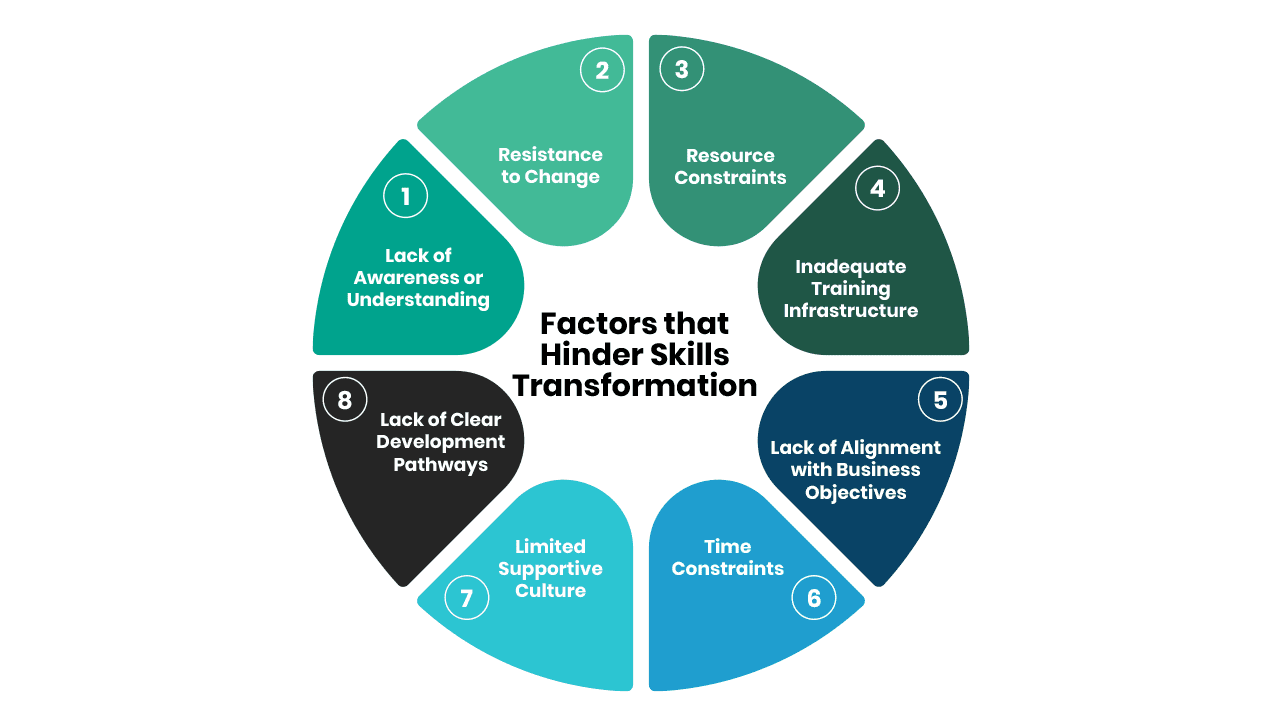
Factors that Hinder Skills Transformation
Considering the importance of Skills transformation to today’s business. There is a need to pay attention to factors that could hinder organisations from making this progress. Here are some common obstacles:
1. Lack of Awareness or Understanding: One of the primary hindrances to skills transformation is a need for more awareness or understanding of its importance. If organisational leaders and employees do not recognise the need for upskilling or reskilling, they may not actively pursue or support skills transformation initiatives.
2. Resistance to Change: Change can be met with resistance, particularly when it involves acquiring new skills or adopting new technologies. Employees may be reluctant to leave their comfort zones or fear their existing skills will become obsolete. Overcoming resistance to change requires effective communication, employee engagement, and addressing concerns or fears related to skills transformation.
3. Resource Constraints: Skills transformation initiatives require organisations to invest time, money, and other resources. Organisations that need to allocate more resources to training programs, hire external trainers, or provide employees with learning opportunities may hinder the progress of this initiative. Limited budgets, competing priorities, or a lack of dedicated training personnel can hinder skills transformation efforts.
4. Inadequate Training Infrastructure: Organisations need proper infrastructure and technology to facilitate skills transformation. Lack of access to training facilities, outdated learning management systems, or inadequate technological resources can impede the effective delivery of training programs. In such cases, organisations may need help providing employees with a conducive learning environment.
5. Lack of Alignment with Business Objectives: To be successful, initiatives focused on skills transformation should align with the strategic imperatives and objectives of the organisation. A mismatch between the developed skills and those required to achieve organisational goals can hinder the effectiveness and relevance of skills transformation efforts. Alignment between skills transformation and organisational priorities is crucial for maximising its impact.
6. Time Constraints: Organisations often face time constraints due to demanding work schedules, tight project deadlines, or high workloads. Finding dedicated time for employees to engage in skills transformation activities, such as attending training sessions or participating in online courses, can be challenging. Balancing the need for skills development with operational demands is a common hurdle.
7. Limited Supportive Culture: A supportive organisational culture is essential for successful skills transformation. Employees may feel discouraged or unsupported in their skills development efforts if the organisation does not foster a culture that values learning, growth, and continuous improvement. Lack of managerial support, a fear of failure, or a lack of recognition for learning achievements can undermine skills transformation initiatives.
8. Lack of Clear Development Pathways: Individuals may need help to prioritise their skill development efforts when they do not have a clear development pathway. They may struggle to identify the most relevant and critical skills for their roles or future opportunities. This challenge can result in a haphazard approach to skill development, where individuals invest time in acquiring skills that may not align with their goals or organisational needs.
In summary, Skills transformation is an ongoing process that allows individuals to adapt to the changing work landscape. The failure to transform the skills set of the workforce can hinder organisational performance, innovation, adaptability, and employee satisfaction. It can also negatively affect the organisation’s competitiveness, market position, and long-term sustainability. Therefore, investing in skills transformation is crucial for organisations to thrive in this dynamic and competitive landscape of the modern world.
At pcl., we have over two decades of experience helping organisations across various industries implement a skills transformation strategy. We also enable organisations to capture and warehouse intellectual assets vital to the success and continuity of their businesses. We have achieved this through our Bespoke Content Digitisation services and Digital Learning Platforms.
We have digitised 100+ interactive and engaging eLearning courses and implemented easy-to-use, safe, and secure digital learning platforms with 120,000+ assets across Africa.
Please speak to one of our consultants via digitallearning@phillipsconsulting.net, and let’s help future-proof your organisation to outperform your competitors.
Written by:

Victoria Debrah
Business Consultant