Executive Summary
In the rapidly evolving digital age, aligning corporate strategy with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is both a responsibility and an opportunity for businesses. This article explores how organisations can leverage digital pathways to contribute to sustainable development, focusing on the crucial role of youth in this transformation. We examine the current landscape, identify challenges, and propose strategic solutions to navigate the future successfully. “The theme “Corporate Strategy for the SDGs: Navigating the Future with Strategic Development” emphasises integrating digitalisation and youth engagement into corporate strategies to accelerate progress towards the SDGs.
Introduction
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, businesses face mounting pressure to contribute to sustainable development. The United Nations’ 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development outlines 17 SDGs to address global challenges such as poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, and peace and justice. With the advent of digital technologies, companies have unprecedented opportunities to drive progress towards these goals.
The advent of digital technologies has transformed our daily lives, work environments, and interactions. Innovations such as artificial intelligence and blockchain offer pioneering solutions to tackle some of the planet’s most pressing issues. Within the framework of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), digital solutions can improve data gathering, optimise resource use, and promote knowledge exchange. Additionally, the growth of the digital economy can generate new employment opportunities, especially for younger individuals who tend to be early adopters of technology. This article discusses the strategic development necessary for corporations to align with the SDGs, focusing on harnessing digital tools and empowering youth.
Youth as Catalysts for Change
Youth represent a significant demographic force with the potential to drive sustainable development. With over 1.8 billion young people worldwide, their engagement is crucial for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). As digital natives, they bring fresh perspectives to global challenges, making their inclusion essential in shaping innovative solutions.
Nigeria, as Africa’s most populous nation, has a particularly strong youth demographic. According to the World Bank, Nigeria’s population was approximately 202 million in 2020, with one of the largest youth populations globally. Individuals aged 0–14 years constitute about 42.5% of the population, while those aged 15–24 years make up approximately 19.6%. This substantial youth segment underscores their critical role in driving sustainable development and contributing to the SDGs.
By empowering young Nigerians and integrating their digital expertise into corporate strategies, businesses can unlock innovation, enhance social impact, and accelerate progress toward sustainable development. Their adaptability, technological proficiency, and problem-solving skills position them as key drivers of change in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Bridging the Gap: Challenges in Implementation
However, despite the vast potential of youth and digitalisation in advancing sustainable development, many organisations struggle to translate these opportunities into actionable corporate strategies. Several challenges hinder the effective integration of digital tools and youth engagement, limiting the impact of businesses in fostering long-term sustainability.
Defining the Problem
Several barriers contribute to this challenge, including:
- Limited Knowledge and Comprehension: Numerous businesses lack a clear understanding of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and their relevance to their activities. This gap in knowledge can hinder companies from recognising ways to engage in sustainable development efforts.
- Insufficient Digital Infrastructure: In many regions, inadequate digital infrastructure limits the potential of digital tools to drive progress. Without reliable internet access and digital literacy, the benefits of digitalisation cannot be fully realised.
- Limited Youth Involvement: Despite their potential, young people often face barriers to participation in decision-making processes. This exclusion can stifle innovation and prevent businesses from leveraging youth’s unique insights and skills.
- Short-Term Focus: Many companies prioritise short-term profits over long-term sustainability. This focus can hinder efforts to integrate the SDGs into corporate strategies and invest in digital tools and youth engagement.
The Role of Digitalisation in Achieving the SDGs
Digital technologies can significantly contribute to various SDGs. For instance:
1. SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): Telemedicine and health applications have significantly enhanced healthcare accessibility, particularly in isolated regions. This innovative approach allows patients in remote areas to consult with healthcare providers through video calls, text messages, or emails, thereby making medical care more convenient and reducing travel requirements for consultations. The rise of telehealth apps has become especially advantageous for individuals who lack easy access to healthcare facilities, which is crucial for those residing in rural or hard-to-reach locations.
In Nigeria, various health applications, such as Omomi and Safermom, have been created to enhance healthcare delivery and improve accessibility. These platforms exemplify how digital solutions are advancing the healthcare sector in Nigeria, contributing to the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal 3 by utilising technology to close the healthcare access gap and enhance health outcomes for marginalised communities.
2. SDG 4 (Quality Education): E-learning platforms have the potential to deliver quality education to marginalised groups. Goal 4 of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) focuses on achieving inclusive and equitable education and promoting lifelong learning opportunities for everyone. By incorporating digital technologies into educational systems, the learning experiences and outcomes can be greatly improved.
pcl. has created digital solutions for various clients to address educational and performance management challenges. One such solution is the deployment of a Learning Platform called Percipio. This intelligent learning experience platform provides an extensive array of resources, including courses, videos, books, and audiobooks, aimed at assisting organisations in upskilling and reskilling their workforce. Through the adoption of this platform, our clients have offered their employees ongoing learning opportunities, which are crucial for their personal and professional growth.
This initiative is in line with SDG 4’s objective to significantly enhance the number of youth and adults equipped with relevant technical and vocational skills, paving the way for employment, quality jobs, and entrepreneurship.
3. SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy): Smart grids and renewable energy technologies play a crucial role in improving energy efficiency and promoting sustainability. The goal of Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG 7) is to provide everyone with access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy. In Nigeria, various initiatives have been launched to adopt smart grid and renewable energy technologies:
- Mini-Grids Development: Nigeria has established numerous mini-grids, frequently utilising renewable energy sources, which serve as an economical solution for providing electricity to rural areas. By the end of 2023, approximately 100 mini-grids had been implemented throughout the country, with many relying entirely or partially on renewable energy.
- Smart Grid Systems: There has been significant research and investment in Nigeria to modernise the power sector with advanced grid technologies. This encompasses the implementation of smart metering, distributed generation using renewable energy, microgrids, and management solutions that leverage Information and Communication Technology (ICT) tools.
- SDG 13 (Climate Action): Digital technologies play a vital role in tracking environmental changes and enhancing climate resilience efforts. In Nigeria, a notable digital solution for monitoring environmental conditions and promoting climate action is the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) digital platform. This platform facilitates the evaluation of potential environmental consequences associated with proposed projects and aids in formulating strategies to mitigate negative impacts. It utilises digital methods like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to gather, manage, and analyse environmental data, which is essential for effective policymaking and project development.
In pcl., we possess expertise in conducting Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA). Our proficiency in this area enables us to generate comprehensive EIA reports that provide valuable information for digital platforms dedicated to environmental monitoring and management. These reports are crucial as they contain detailed analyses of potential environmental impacts of proposed projects and recommend mitigation strategies to minimise adverse effects.
Youth Engagement and Innovation
Research shows that youth engagement can lead to innovative solutions for sustainable development. For example, young entrepreneurs are developing apps and platforms that address various SDGs, from reducing food waste (SDG 12) to promoting gender equality (SDG 5). Furthermore, organisations involving young people in decision-making benefit from diverse perspectives and increase creativity.
Stated below are a few examples of young entrepreneurs in Nigeria who have developed applications and platforms to address SDGs:
- Temie Giwa-Tubosun – Founder of LifeBank, an app that connects blood banks with hospitals to ensure timely delivery of blood supplies, addressing SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being).
- Bilikiss Adebiyi-Abiola – Co-founder of Wecyclers, a platform that incentivises waste recycling in Lagos, promoting SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
- Temilade Salami – Founder of EcoChampions, a youth-led organisation promoting environmental sustainability and climate action. Through EcoChampions, she engages young people in activities such as tree planting, environmental education, and waste management, addressing SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
- Chris Kwekowe – Co-founder of Slatecube, a platform that offers virtual internship opportunities and skills development for young people, contributing to SDG 4 (Quality Education) and SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
- Samson Abioye – Co-founder of Pass.ng, an e-learning platform that helps students prepare for exams, thus supporting SDG 4 (Quality Education).
- Yusuf Bashir – Founder of KAD ICT Hub, which provides training and support for young entrepreneurs in Kaduna, Nigeria, contributing to SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
Recommendations
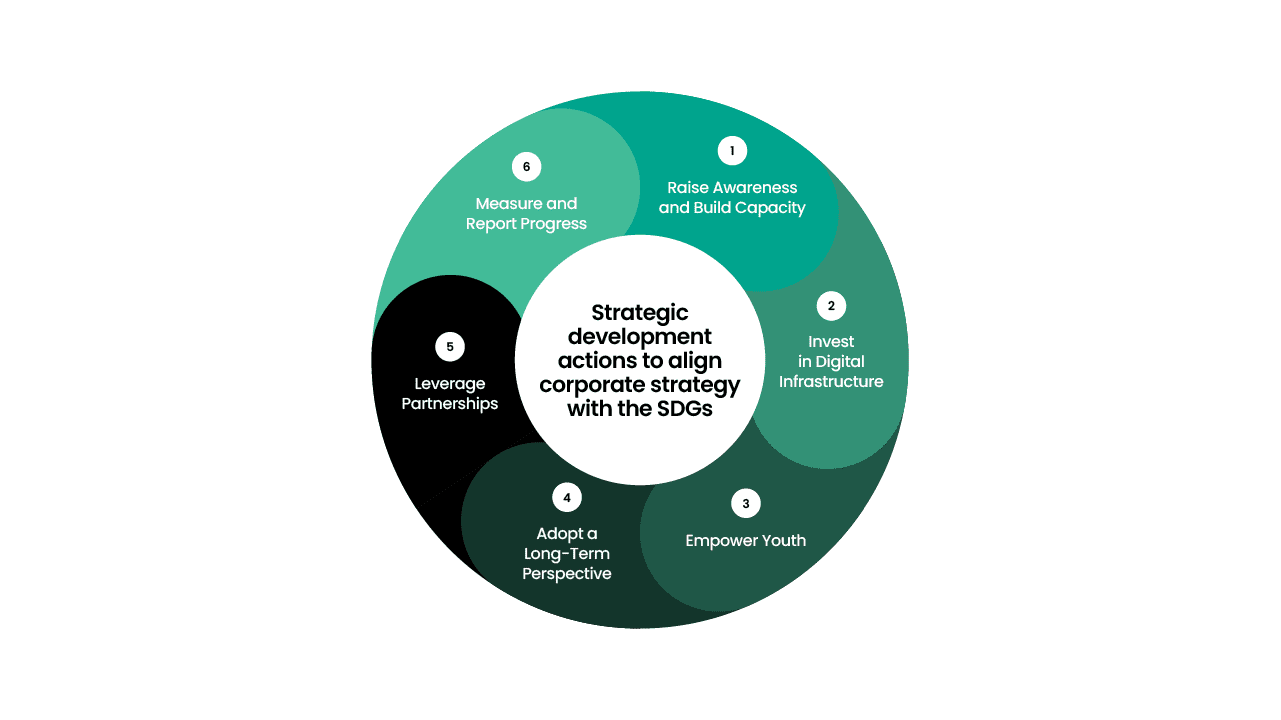
To navigate the future and align corporate strategy with the SDGs, businesses should consider the following strategic development actions:
- Raise Awareness and Build Capacity: Companies should invest in educating their workforce about the SDGs and the importance of sustainable development. This can be achieved through training programmes, workshops, and partnerships with organisations specialising in sustainability.
- Invest in Digital Infrastructure: Businesses should prioritise investing in digital infrastructure to ensure reliable internet access and digital literacy. This investment can enhance the effectiveness of digital tools and enable more people to participate in the digital economy.
- Empower Youth: Organisations should actively involve young people in their strategic development processes. This can be done by creating platforms for youth engagement, offering mentorship programmes, and supporting youth-led initiatives.
- Adopt a Long-Term Perspective: Companies should prioritise long-term sustainability over short-term profits. This shift requires integrating the SDGs into corporate strategies and aligning business goals with sustainable development objectives.
- Leverage Partnerships: Collaboration with other organisations, governments, and civil society can amplify efforts to achieve the SDGs. Partnerships can facilitate knowledge sharing, resource pooling, and coordinated action towards common goals.
- Measure and Report Progress: To ensure accountability, businesses should establish metrics to track their progress towards the SDGs. Regular reporting can provide transparency and demonstrate commitment to sustainable development.
Conclusion
In the digital age, aligning corporate strategy with the SDGs is essential for businesses to thrive and contribute to a sustainable future. By harnessing digital tools and empowering youth, companies can drive innovation, enhance sustainability, and create shared value. The theme “Corporate Strategy for the SDGs: Navigating the Future with Strategic Development” highlights the transformative potential of digitalisation and youth engagement. By adopting strategic development actions, businesses can navigate the future successfully and play a pivotal role in achieving the SDGs.
Here at pcl., we believe young minds and digital solutions are crucial to achieving the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). But clicks alone won’t get us there. We invite businesses, partners, and stakeholders to join us in this mission by:
- Integrating SDGs into your Core
- Empowering Your Workforce
- Fueling Youth Innovation
- Collaboration is Key
- Reporting and Communicating Your Progress
Together, let’s Navigate the future with strategic development. Contact us at sot@phillipsconsulting.net or call +2349060000804 to learn and explore how your business can contribute to a sustainable future.
Written by:
Omoyosola Odukoya
Senior Analyst