If there’s one thing banks have in abundance, it is data, and Nigerian banks are no exception. According to Forbes, over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are generated globally daily. Not only the type of data you may be conversant with but data across various sources and systems, from ATMs to traditional credit processing parts of the business. Previously, available financial data was restricted to collecting basic customer information such as name, address, and transaction history. However, financial institutions now have access to massive volumes of invaluable, first-party customer data generated by their mobile applications, web portals, and other digital resources.
Concurrently, there’s a continued push for collecting even more data through open-data initiatives and financial data sharing. While this high influx of information can bring more profound insights into customer behaviour, internal operations, and the industry, its ultimate value relies heavily on how that data is assembled, processed, stored, and interpreted through business intelligence in banking.
Banks in Nigeria must adopt business intelligence to help with their data because financial institutions must implement sound business intelligence practices as promising as the big data revolution to ensure profit is realised. This can be possible only if they leverage business intelligence tools, as this brings disparate data from various applications and creates a unified source of information that anyone in the company can utilise. The banking industry faces rising competition, risk management, and ever-changing customer demands. However, with the help of BI tools, they can leverage customer data to derive valuable insights, help with analysing trends, identify patterns, and be equipped with real-time reporting to make better financial operations and decisions.
What is Business Intelligence?
According to Oracle, Business intelligence (BI) refers to capabilities that enable organisations to make better decisions, take informed actions, and implement more-efficient business processes. Business intelligence (BI) refers to software technologies, applications, and practices for collecting, integrating, analysing, and presenting business information. Business Intelligence is also a tool that salvages, assembles, accumulates, and processes the data to provide constructive input to the organisation that helps in better decision-making. Business Intelligence tools are software that uses databases to generate informative reports for decision-makers. It is an information source and a firm decision support system useful to organisations in developing ideas for growth in today” s competitive market scenario.
The term “Business Intelligence” was coined by Hans Peter Luhn (1958), who defined it as “the ability to apprehend the interrelationships of presented facts in such a way as to guide action towards a desired goal.” Forrester Research defines business intelligence as “A set of methodologies, processes, architectures, and technologies that transform raw data into meaningful and useful information used to enable more effective strategic, tactical, and operational insights and decision-making.”
Banking and Business Intelligence
Business intelligence in banking is using analytics software, or SAAS (software as a service), to create interactive data visualisations to drive intelligent decisions for the betterment of the organisation. In Nigeria, most banks have adopted business intelligence. However, some banks excel in it more than others, as the complexity of business intelligence depends on the size of the bank in terms of staff, data, etc. Adopting business intelligence is expensive, but the results are fruitful as it makes the operations cost-effective.
In Nigeria today and worldwide, fulfilling customers’ expectations is critical in the banking sector, and as such, it needs to focus on business intelligence to achieve customer satisfaction. The BFSI (Banking, Financial Sector and Insurance) sector in Nigeria has dealt with people with diverse behaviour and mindset. Not only the customers but the multi-segment nature of today’s banking where there is an overlap of customer base. It is necessary to integrate these various segments to ensure efficiency and effectiveness. Thus there is a severe need for business intelligence. This helps in creating a unique entity by compiling and integrating multiple components.
The banking sector in Nigeria has changed a lot, especially with the growing change; banks must strengthen their system to conform to the evolution of business processes to ensure they do not pack up as a business. Business intelligence is a tool for the progression of this industry. In the early days, the banking system was cost-ineffective, labour-intensive, and not customer friendly; hence, there was hardly an effort to know the kind of service a customer wanted. With time they grew in size, operation, dealings, etc. Manual working became redundant. As time passed, they developed differentiated products ad multi-segmentation to provide the customer with a one-stop-shop solution. This diversity needs to streamline its data for smooth working and coordination; this is where business intelligence plays an important role.
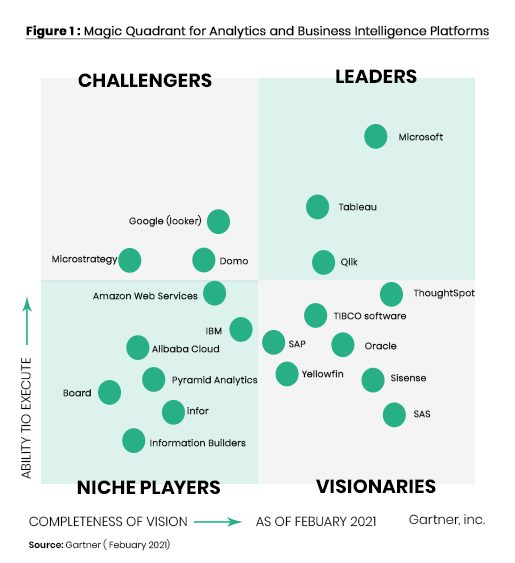
Intelligence and competence are obligatory for processing and mining a plethora of data. The right technology, culture, and processes should be in place to make it effective. But as has been realised, the genuine gain from such investigative tools can be brought to fruition only if appropriately utilised. Over the years, the increasing popularity of automated teller machines (ATMs) revolutionised banking and finance, reducing the teller personnel required for each branch and allowing thousands of new ATMs to open. Some banking business intelligence software mainly used in Nigeria today and globally includes Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, Tibco Spotfire, and Domo. These banking business intelligence applications can be hosted on the cloud or set up to run on private dedicated servers for financial services companies that are strict on data security requirements. In February 2021, Gartner released a report showing the best software/application in the Business intelligence field in terms of their strengths and offerings.
Benefits of Business Intelligence to Banks
Improved Customer Experience and Retention:
Data is essential for developing customer segmentation and optimised omnichannel communication to deliver hyper-personalised and timely customer content. BI in the banking sector can provide the banking industry with the technological resources it might need by presenting more targeted offerings, improving customer experience, and maximising cross-selling and upselling opportunities.BI tools help financial companies identify and understand why customers leave to patronise the competition. They reveal what the customers desire from a product or service. With this, companies can come together to provide improved products and services while increasing customer retention and experience. Banks can develop more cost-effective ways of interacting with money-losing customers with customer profitability information. For example, if educated on the benefits, a customer can be advised to use online banking to pay bills rather than making cash withdrawals from the bank to pay bills. Online banking is cheaper than teller transactions involving a human to track customer habits, preferences, and behaviours. Implementing BI enables banks to customise their products and services to meet needs, solve problems, and promote and increase customer retention, experience, and loyalty.
Enhance Internal Operation:
Since banks cannot afford to employ staff to increase revenues, they have to continually strive for a means to automate their existing workforce to be more effective. BI solutions for banks and other financial bodies can analyse operational processes to help reduce ongoing costs and Improve current organisational resources and capabilities. A good example is analysing your branch personnel’s performance regarding interfacing with your customers. Using a BI tool, the bank can find ways to improve and enhance the customer experience at the point of contact.
By examining throughput volume, service delivery cycle time, mistake rates, and service quality CSATs, business intelligence in the banking sector aids in tracking the performance of various departments and staff. Organisations gain an understanding of their operational processes using this information. Take this as a case study. Banks use business intelligence to identify consumer needs and how their staff can meet them. They can provide a better consumer experience as a result. Your internal operations’ effectiveness matters as much as how customers perceive your business. Using business intelligence software solutions is a data-backed method for evaluating resource allocation, operational processes, and personnel performance. Your data can show you where to improve expense savings and customer experience.
Risk Management:
Business intelligence solutions can help you reduce risks by enabling you to use data to make decisions. You can immediately identify fraudulent actions by monitoring client behaviour. Additionally, you may ensure that employees follow industry regulations by observing their behaviour. You can also evaluate credit portfolios and look for potential signs of delinquency using the available data and information about the current state of the economy. Banks’ compliance with local, national, and worldwide regulatory norms can be ensured through a reliable BI. The financial institution can produce and extract real-time reports, graphs, tables, and dashboards to track performance in real time with the help of a wide variety of reporting templates. Implementing Business intelligence in your organisation will help you conduct risk assessments, keep track of incidents, occurrences, and actions, Manage data for audits, inspections, and investigations, control documentation, and facilitate personnel inductions, training, and competency evaluations. The risk variables will diversify significantly as the banking industry becomes more intricate and integrated. The most significant risk that banks need to reduce is undoubtedly fraud. Looking out for nefarious activity when using credit cards and checking accounts is vital. The likelihood of lawsuits and theft can reduce by monitoring employee behaviour for questionable purchases, withdrawals, expenditures, and lending. Examining past dues and repayment activity may reveal patterns like an economic slowdown. Using business intelligence technologies is a proactive strategy to reduce risks in the financial industry. The financial sector is prone to abrupt and uncertain shifts. To mitigate risks, BI applications in the banking and financial industry assist in the detection and reduction of fraudulent activity
Improved Marketing:
Banks will be at an advantage in selling to prospects if they have access to household profitability and demographic data since they will be more familiar with what makes a good prospect. By understanding their target market before making a marketing appeal, banks can develop cross-sell and up-sell more successful campaigns. The benefit is significant since research has shown that selling to current customers is five times less expensive than finding new ones. Customer relationship management (CRM) data can offer insight into the success of marketing initiatives. Identifying customer-resonance hotspots and areas for improvement is possible with BI by looking at email performance, advertising spending, and overall campaign success.
Faster Real-Time Reporting:
Banking BI allows organisations to visualise real-time historical and current data. It will enable clear visualisation in spotting patterns and potential bottlenecks, setting goals more straightforwardly based on historical metrics, and no more waiting for a report for two months after you requested it from finance. Business Intelligence in the banking sector visualises the company’s historical and current data to identify customer behavioural patterns and potential blockages in the system. With real-time visibility into operations, they offer the proper insight across the use of resources, teller performance, counters, and wait times to get a live snapshot of appointments. It provides visual cues to take necessary actions to achieve goals. This data will be filtered by location, bank branch, products, offerings & transaction types to identify the areas required for maximum effectiveness.
In conclusion, Business intelligence is no longer a nice to have in the banking industry in Nigeria; it is very critical for all financial institutions in Nigeria to optimise performance, improve profits, or streamline business functions.
Written by:

Ogonna Okorie
Senior Analyst