Introduction
In a bustling village in Nigeria, where the sun rises over the acacia trees and the mornings are filled with the sounds of nature, a young girl named Amina dreams of becoming a doctor. Every day, she walks miles to the nearest school, her heart filled with determination and her mind buzzing with the desire to learn. But Amina faces a significant challenge: her school has no access to digital technology. While students in more developed regions of the world have the internet at their fingertips, enabling them to access endless information and resources, Amina’s education is limited to the few books available in her small classroom.
Amina’s story is not unique. In today’s interconnected world, digital technology is the backbone of modern society, driving economic growth, fostering innovation, and enabling access to information and services. However, the benefits of the digital age are not evenly distributed. The digital divide, a term used to describe the gap between those with access to digital technologies and those without, remains a significant barrier to achieving global equity. This divide exacerbates existing inequalities, particularly in education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
Consider the contrast: In a city across the globe, a boy named Ethan wakes up in his comfortable home in New York City. He logs onto his laptop, attends virtual classes, accesses a wealth of online resources, and participates in interactive lessons. The world is at his fingertips, and he has the tools to explore his interests, connect with experts, and build a bright future.
The stark difference between Amina and Ethan’s experiences highlights the urgent need to address digital inclusion and equity. Bridging this digital divide is crucial for building a sustainable and inclusive future where every child, regardless of their geographic location, has the same opportunities to succeed. Addressing digital inclusion and equity is, therefore, crucial for building a sustainable and inclusive future. This article explores strategies to bridge the digital divide, supported by case studies demonstrating successful implementations.
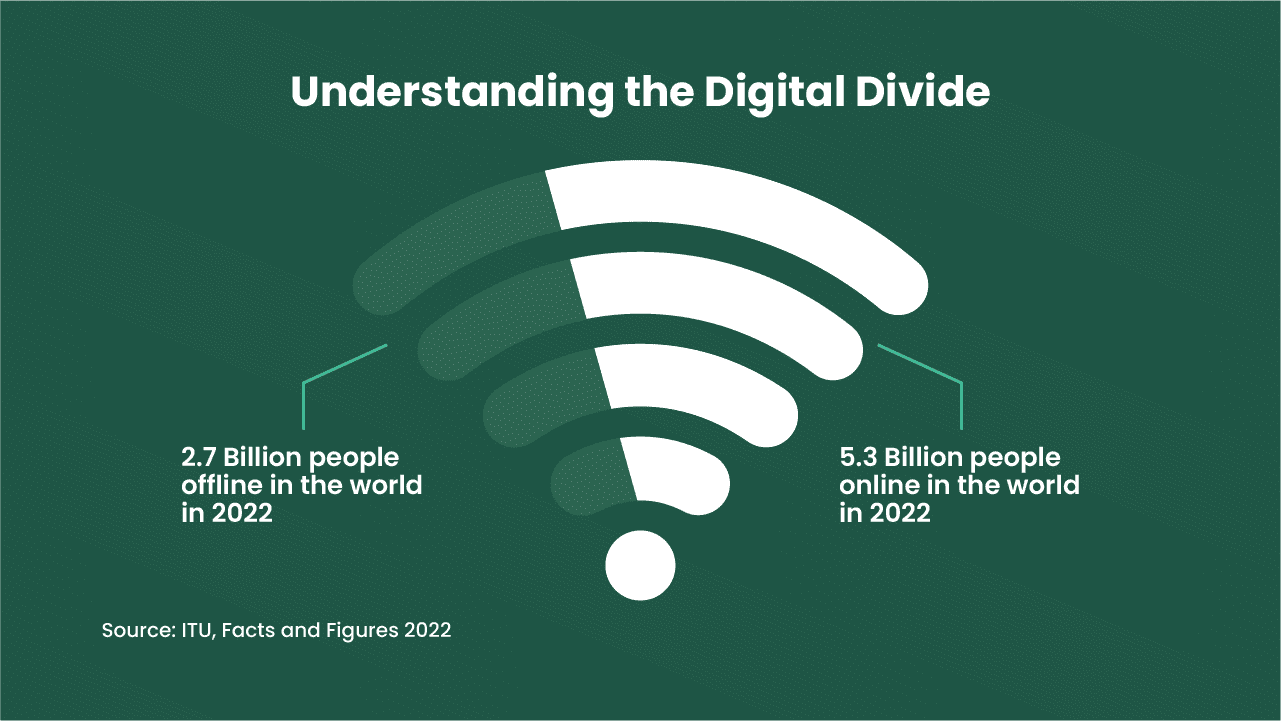
Understanding the Digital Divide
Globally, approximately 2.7 billion people lack internet access, according to the World Economic Forum 2023. This 2.7 billion people, or one-third of the world’s population, who remain offline today mostly reside in low-income communities or remote areas with limited broadband service. Over the past decade, increased collaboration between businesses, governments, inter-governmental organisations, and non-governmental organisations (NGOs) has narrowed the digital divide. However, the inequality gap between those with computer and internet access and those without is widening.
Bridging this divide requires collaborative efforts between governments, businesses, and organisations. The digital divide encompasses various dimensions, including access to devices, connectivity, digital literacy, and the availability of relevant content and services. It is prevalent across different demographics, including rural and urban populations, low-income households, and marginalised communities. The consequences of the digital divide are far-reaching, impacting educational outcomes, job prospects, access to healthcare, and overall quality of life.
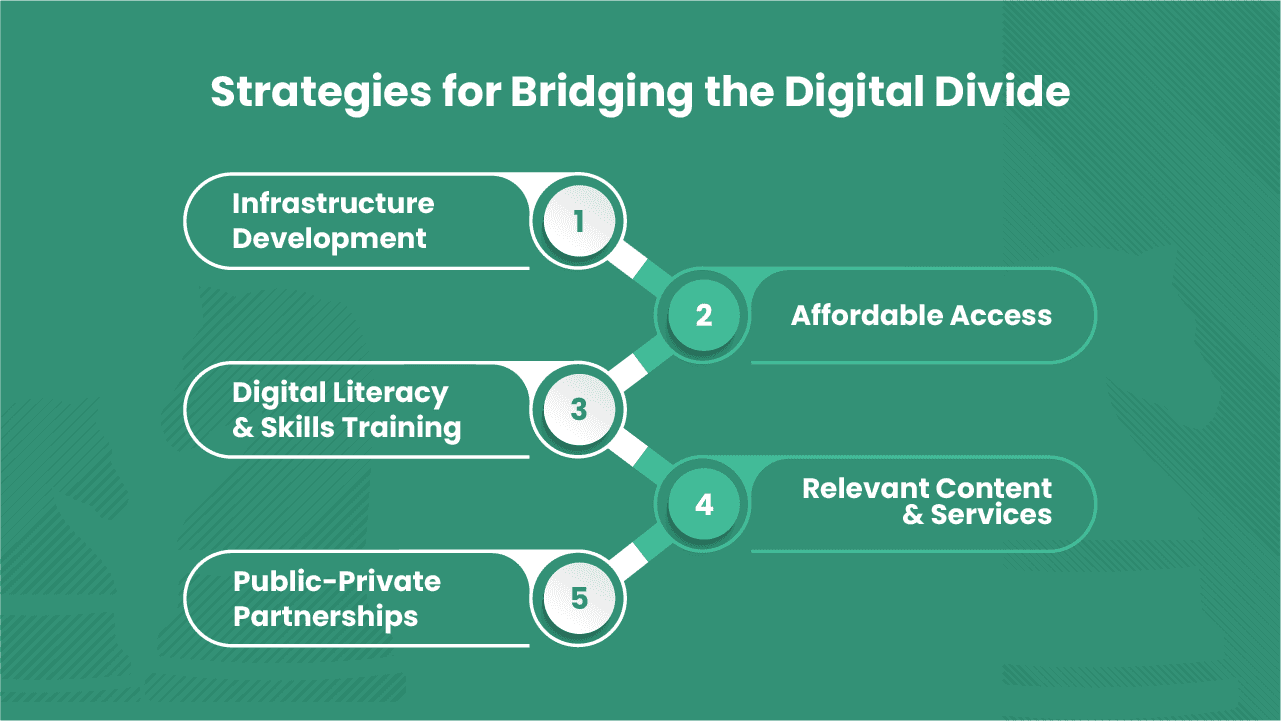
Strategies for Bridging the Digital Divide
-
Infrastructure Development
One of the primary barriers to digital inclusion is the lack of infrastructure, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Investing in robust and widespread broadband infrastructure is essential. Governments and private sector partnerships can play a pivotal role in expanding connectivity. An example of efforts to bridge the digital divide through infrastructure development is the “Computers for All Nigerians Initiative (CANI),” supported by the Intel® World Ahead Program. This initiative aims to increase digital inclusion by making technology more accessible to Nigerians.
One major aspect of the CANi initiative is infrastructure expansion. The capital city of Abuja was covered by a high-speed WiMAX network, significantly improving internet access in the area. This has had a major impact on the youth in the area due to the strong internet connectivity.
-
Affordable Access
Even with available infrastructure, affordability remains a significant hurdle. Many individuals and families cannot afford internet services or digital devices. Subsidies, low-cost service plans, and community access points can help mitigate this issue. An example is the “DigiGap Program”, which is in partnership with Access Corporation and seeks to create learning and economic opportunities, promote digital and technology careers, and bridge the digital gap among young Nigerians. It is a Nigerian government initiative designed to improve internet access among young people, particularly in low-income and rural areas. Recognising the critical role that the Internet plays in education, employment, and social engagement, DigiGap focuses on providing affordable access to digital tools and connectivity for youth.
Since its launch, DigiGap has significantly increased internet access among Nigerian youth, particularly in regions where connectivity was previously a major barrier. By making digital tools and internet access more affordable, the program is helping to create more equitable opportunities for young people across Nigeria, laying the foundation for a more inclusive digital economy.
-
Digital Literacy and Skills Training
Access to technology is only part of the solution. Digital literacy is the ability to effectively and safely use digital tools. This is essential for meaningful participation in the digital world. Programs focused on digital skills training can empower individuals to leverage technology for personal and professional growth. An example is the “Technology for Social Change and Development initiative (Tech4Dev)”, which partnered with the Federal Ministry of Youth and Sports Development to upskill 36,000 young Nigerians in digital and technology skills through the Emerging Markets Model Initiative (EMMI) powered by Microsoft Philanthropies. This initiative was to bridge the digital gap by creating access to decent work, entrepreneurship opportunities, and platforms for Africans through digital skills empowerment and advocacy, thereby creating a more digitally inclusive Nigeria.
-
Relevant Content and Services
For digital inclusion to be meaningful, the content and services available online must be relevant and accessible to diverse populations. This includes providing content in multiple languages, catering to local needs, and ensuring accessibility for individuals with disabilities.
-
Public-Private Partnerships
Collaboration between governments, private companies, and non-profit organisations can amplify efforts to bridge the digital divide. Public-private partnerships can leverage resources, expertise, and innovation to create sustainable solutions.
The Microsoft Airband Initiative partners with internet service providers, energy access companies, and local entrepreneurs to extend global broadband access to underserved rural areas. The initiative focuses on leveraging TV white space technology, solar power, and other innovative solutions to deliver affordable internet services. By 2022, Airband had connected over 24 million people in rural areas, demonstrating the power of collaborative efforts to bridge the digital divide.
Moving Towards a Sustainable and Inclusive Digital Future
Bridging the digital divide is a technological challenge and a societal imperative. Ensuring digital inclusion and equity requires a multifaceted approach that addresses infrastructure, affordability, digital literacy, relevant content, and collaborative partnerships. The case studies highlighted above demonstrate that with concerted efforts and innovative solutions, it is possible to make significant strides toward digital inclusion.
Conclusion
As we move further into the digital age, the importance of addressing the digital divide becomes increasingly apparent. Digital inclusion is essential for achieving social equity, economic development, and sustainable growth. By implementing strategies that enhance infrastructure, affordability, digital literacy, and collaboration, we can create a future where everyone, regardless of their background or location, can participate fully in the digital world.
As we’ve seen through initiatives like the DigiGap Program and the Tech4Dev, targeted efforts to improve digital literacy and affordable access can profoundly impact young people, particularly those in underserved communities. By equipping youth with the necessary skills, tools, and connectivity, we can empower them to participate fully in the digital economy, drive innovation, and secure better futures for themselves and their communities.
Written by:
Chidubem Ugo
Analyst
![]()