In the dynamic landscape of consumer preferences, the undeniable appeal of e-commerce has surged dramatically, driven by its numerous advantages—convenience, variety, and seamless comparison options. However, despite these strengths, e-commerce falls short of fostering meaningful brand-shopper relationships. A transformative shift is underway with the rise of social commerce, a dynamic blend of community and communication reshaping online shopping.
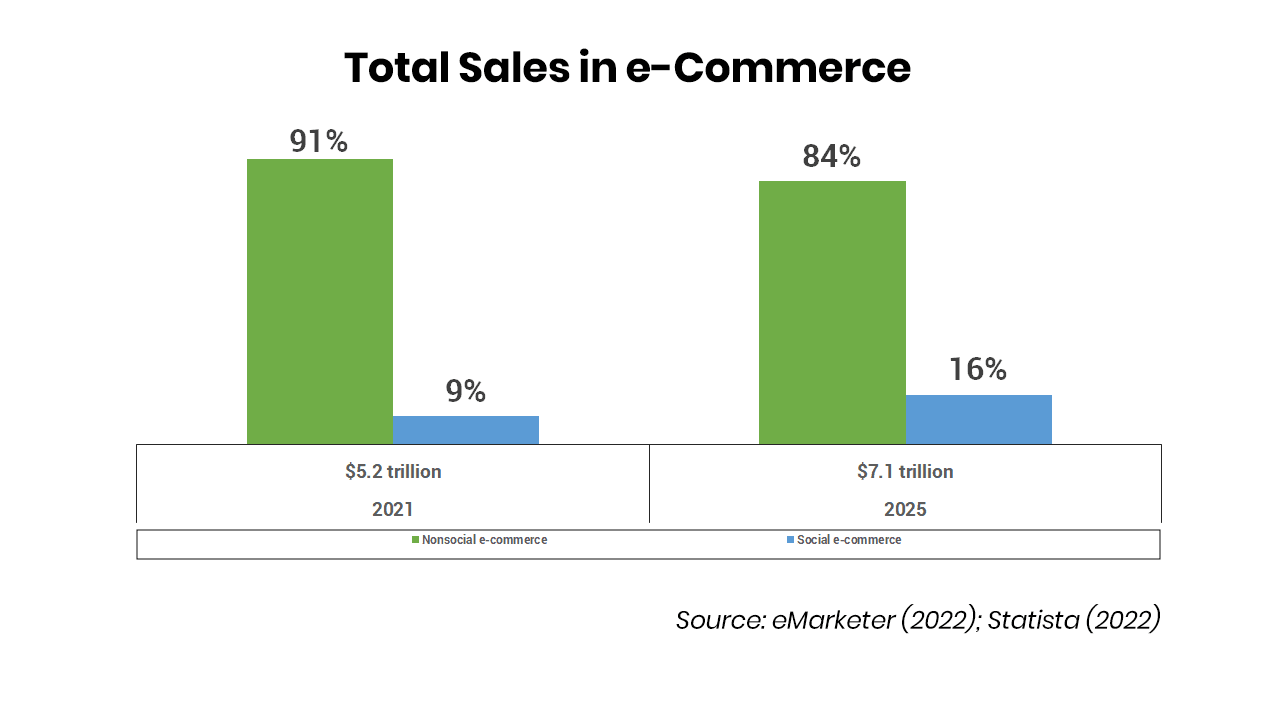
According to data from Statista and Emarketer, the global social commerce market is projected to reach $1.14 trillion by 2025, up from $468 billion in 2021.
Figure 1: Total Sales in e-Commerce
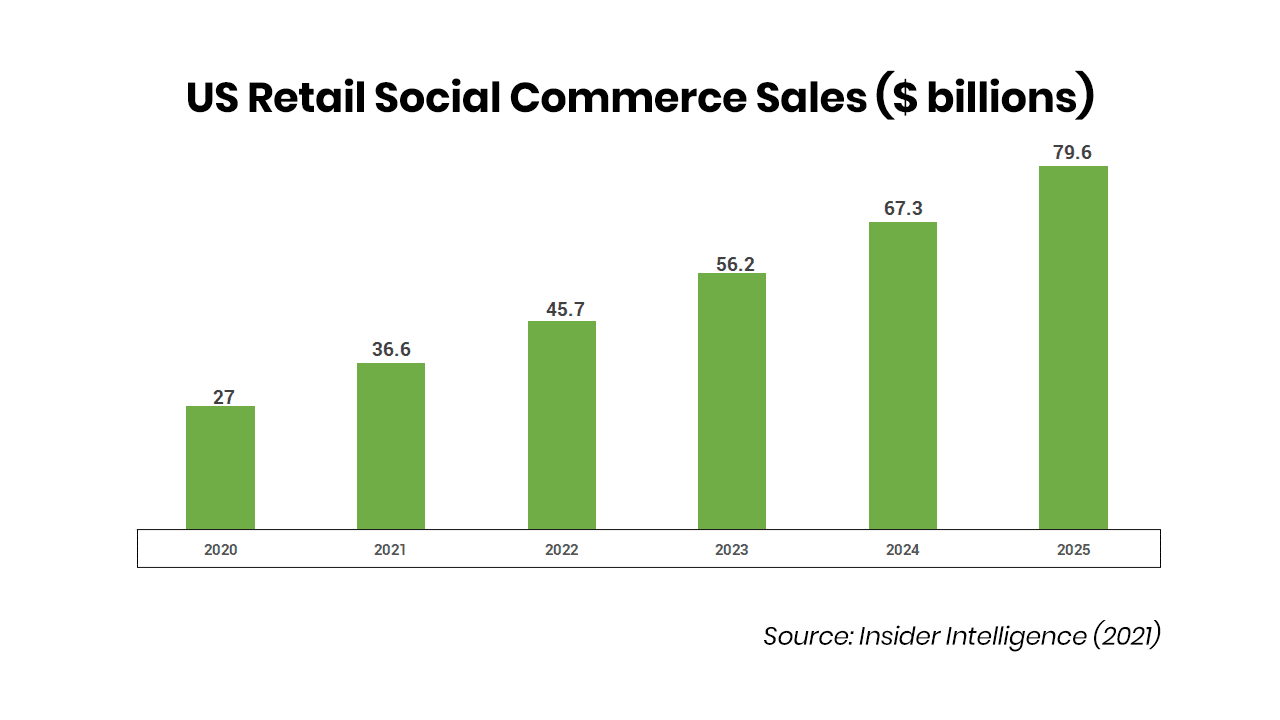
Since 2016, social commerce in China has soared, with a 52% increase to over $350 billion in transactions by 2021—representing 13% of Chinese e-commerce sales. Already enormously popular in markets such as China, social commerce remains a small but rapidly growing segment in the United States. In 2021, $37 billion in goods and services were purchased through social-commerce channels (Insider Intelligence, 2021). By 2025, that figure is expected to swell to nearly $80 billion, or 5% of US e-commerce. (Statista, 2022).
Figure 2: US Retail Social Commerce Sales ($ billions)
Social commerce is surging, with global sales on social media platforms expected to reach $1.298 billion in 2023 and a staggering $3 trillion by 2026 (Statista, 2023). China is at the forefront of this trend, with an impressive 84% of consumers making purchases through social media in 2022. In the US, approximately 36% of internet users, totalling around 90 million consumers, actively use social buying on at least one platform.
Nigeria is experiencing a notable rise in social commerce, driven by its 33 million active social media users. The country’s e-commerce market is projected to reach $75 billion by 2025, a significant leap from $12 billion in 2018. This growth is fueled by increased internet penetration, widespread smartphone adoption, and a young, digitally savvy population. Despite the potential, a recent report from Techpadi highlights a downside, revealing scams amounting to N357 million between 2020-2021, particularly impacting those purchasing from Instagram sellers. Nevertheless, Nigeria boasts a robust social media presence with 44 million users and holds the highest global engagement minutes, signalling a promising social commerce landscape.
Social commerce, the seamless integration of social media platforms and e-commerce, enables users to explore, discover, and directly purchase products or services within their favourite social apps. This convergence of social networking and online shopping creates a cohesive shopping experience within a social environment, leveraging user influence, user-generated content, and social recommendations to drive sales and engagement. The global impact of social media, with billions of users on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Pinterest, has fundamentally altered how people connect, share, and discover content.
Social media’s impact extends to consumer behaviour as individuals increasingly turn to their social networks for product recommendations, reviews, and inspiration. Businesses now have the opportunity to harness this social influence and convert it into sales through social commerce. Social commerce offers businesses multiple advantages. Firstly, it provides a direct channel for engaging with the target audience in real-time, allowing companies to promote products, share updates, and interact with customers for a personalised shopping experience. Secondly, it enables businesses to build trust and credibility by leveraging user-generated content, such as reviews, testimonials, and influencer collaborations, serving as social proof that influences the purchasing decisions of potential customers.
The benefits extend to a simplified and convenient purchasing process for consumers, who can discover, read reviews, and make purchases all within the same platform, eliminating the need to switch between multiple apps or websites. Additionally, social commerce delivers personalised recommendations based on individual preferences, purchasing history, and social connections, creating a tailored shopping experience for each customer. Despite its potential, social commerce faces noteworthy challenges. Privacy and data security issues arise due to the substantial collection of user data, emphasising the need for transparent privacy practices to cultivate consumer trust.
Trends Reshaping the Retail Landscape of Social Commerce
In the dynamic realm of social commerce, the retail landscape is in a perpetual state of evolution, marked by the continuous emergence of new trends. Currently, five trends are notably reshaping the social commerce retail experience:
- Influencer Marketing: While influencer marketing is not new, its significance in social commerce is growing. Retailers increasingly rely on social media influencers to expand their reach and endorse products authentically, leveraging the influencers’ connection with diverse audiences.
- Live-Stream Shopping: Live-stream shopping is gaining prominence as an effective means of engaging customers and boosting real-time sales. Retailers utilise live streams to conduct product demonstrations, host Q&A sessions, and provide behind-the-scenes glimpses, offering customers a comprehensive preview of their potential purchases.
- Shoppable Posts: Shoppable posts have revolutionised the retail landscape by allowing customers to click on a featured product within a post and seamlessly navigate to the retailer’s website for immediate purchase. This streamlined process eliminates the need for customers to search for products manually, significantly enhancing the likelihood of purchasing.
- Micro-influencers: While major influencers continue to hold sway, the rise of micro-influencers is noteworthy. These individuals may have a smaller following, but their engaged audience often translates into a higher conversion rate. Brands recognise the authenticity that micro-influencers bring to product promotion and are increasingly tapping into this segment.
- Social Audio: Social audio, represented by platforms like Clubhouse, Twitter Spaces, and Facebook Rooms, is the latest frontier in social media. Social audio is gaining traction among retailers, enabling users to participate in live audio conversations on various topics individually or in groups. Businesses are exploring the potential of social audio to foster intimate interactions, build communities, and uniquely promote products within this novel medium.
How Companies Could Leverage Social Commerce
Organisations should perceive a social commerce initiative as a novel strategy integrated into their existing e-commerce frameworks by directly and engagingly addressing how their products cater to customers’ needs. As a foundational step, brands and retailers must enhance their core e-commerce capabilities. This involves elevating their proficiency in social media marketing and fostering integration between e-commerce and marketing by implementing focused pilot initiatives on selected social platforms.
Crucially, companies should conduct preliminary assessments with target consumers. Initial campaigns may involve the incorporation of shoppable links on platforms like Instagram or Pinterest, coupled with reward programs that provide discounts or award points when a customer’s referral results in a purchase.
During this phase, organisations should lay the groundwork for more sophisticated social-commerce endeavours by proactively tackling three potential challenges:
- Regulatory Constraints: Due to existing and evolving data privacy regulations, brands must exhibit creativity in incentivising consumers. This could involve offering rewards such as discounts on future purchases or access to the full functionality of the social-commerce site in exchange for permission to collect data about their online activities.
- Technical Boundaries: Antitracking measures can hinder the personalisation of product recommendations and disrupt a seamless social-commerce experience. To foster user engagement, brands must explore innovative solutions, including strategic partnerships with tech industry leaders and expanding their data capabilities to construct comprehensive customer profiles, thereby improving recommendations and streamlining the shopping process.
- Consumer Sentiment: Negative perceptions could arise if influencers associated with a social-commerce site exhibit questionable behaviour, such as endorsing controversial stances or engaging in inappropriate public activities. Companies must carefully negotiate agreements with influencers and other channel partners to mitigate this risk, emphasising their alignment with the brand image. Regular reviews of these arrangements are essential to ensure ongoing appropriateness.
Conclusion
The retail landscape is transforming profoundly in the dynamic convergence of e-commerce and social commerce. While e-commerce excels in convenience, variety, and comparison options, social commerce is the catalyst for fostering authentic brand-shopper relationships. The exponential growth projected in the global social commerce market underscores its rising influence. Companies should seamlessly integrate social commerce into existing e-commerce structures, addressing challenges like privacy concerns and technical boundaries. As trends like influencer marketing and live-stream shopping redefine the retail landscape, businesses must embrace this transformative shift or risk being left behind. Seamlessly integrating social commerce into existing structures is more than just a strategy; it is an imperative for those poised to lead the next wave of retail innovation. The future belongs to those who navigate the challenges with strategic prowess, leveraging the power of social commerce to create unparalleled, authentic connections with consumers.
Written by:
Temitope Abimbola
Research Associate