Today’s business environment requires continuous and impactful innovations and innovative thinking due to the constant digital, economic, and environmental transformation affecting business operations.
As the need for innovation increases, the challenge of aligning these innovations with changing market dynamics and existing strategies also increases. Time and money are not the only necessary investments required to develop or implement innovation; a Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Timely (SMART) innovation strategy must also be deployed to support innovation. The absence of a SMART innovation strategy may lead to a failure to execute innovative ideas or a lack of sustainability in the performance of previously successful innovations or innovators, which may negatively impact a business.
The lack of innovation strategy efforts goes beyond a failure to execute; they also include a failure to plan and adapt effective strategies. A strong strategy will help promote an alignment between innovation and market dynamics, clarify objectives and priorities, and help focus efforts on them.
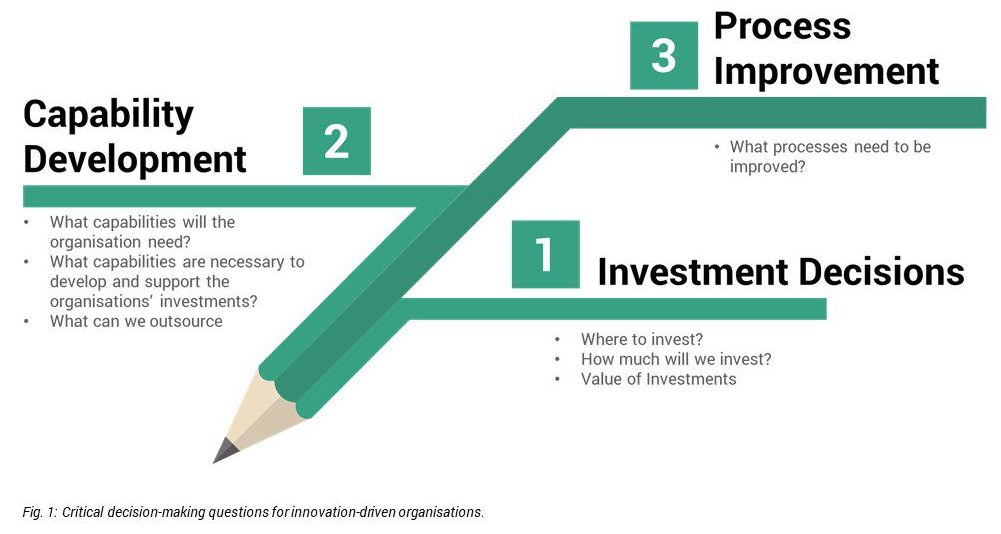
Innovation Strategy provides innovation-driven organisations with a framework for critical decision-making processes related to innovation, as depicted below:
Five (5) questions must be asked while developing a SMART innovation strategy.
-
Why Innovate?
The planning process of your innovation strategy begins with defining your organisation’s objectives by asking questions such as, “what do you aim to achieve with innovation? How can innovation support your business ideas?”. An organisation’s approach to developing an innovation strategy should be rooted in these questions. Policies to innovation strategy vary by company needs; however, there are two effective approaches to innovation strategy, business model innovation and leveraging existing business model.
- Business Model Innovation: This is a blue ocean strategy approach to innovation. As the blue ocean strategy dictates, it is the conceptualisation of new and unique concepts to support an organisation’s financial viability, including its mission and the processes for implementing the developed strategy. The key goal of business model innovation is to address the choice of target clients, products/or service offerings and revenue generation model.
- Leveraging Existing Business Model: This refers to the continuous improvement of established innovations by leveraging existing business models. This model differs from Business model innovation because it focuses on improving the current business models instead of building new business models to create new value.
-
Who is your ideal client, and Who are your existing competitors?
The next step in developing a SMART innovation strategy is defining your organisation’s target market and identifying your proposed value compared to existing competitors’. Understanding your organisation’s unique value proposition will assist in determining your innovation strategy.
-
What value do you propose?
Defining your organisation’s unique value proposition will further help identify how your organisation will win and the types of innovations that will support the organisation’s drive for value creation and competitive advantage development.
-
What are your core capabilities? What gaps need to be filled?
After identifying your organisation’s unique value proposition, the next step will be to assess your core capabilities, including organisational culture, Research and development, Core values, Knowledge base, and existing Skills. The successful execution of an innovative strategy is mainly dependent on its ability to implement successfully. Implementation is largely reliant on the core capabilities of the organisation.
-
What innovation technique and systems do you need to execute your innovation strategy?
Finally, it is essential to identify the most critical technical and operational structures that need to be put in place to ensure a successful implementation.
Procter and Gamble (P&G), an American multinational consumer goods company, was established under a progressive and innovative culture. Right from its inception in 1837, the organisation’s co-founders continuously sought ways to develop original products that would tend to the needs of its target market. P&G adopted both approaches to innovation strategy; they explored new and innovative ideas while also leveraging existing business models to keep them ahead of the competition.
In 2000, the CEO of Procter & Gamble Company, A.G. Lafley, began a transformative culture that sought to make innovation part of the daily routine and establish an innovation culture. The collection of innovative ideas was no longer limited to the research and development team; it became a company-wide social system that sought to leverage the skills and insights of people throughout the company and give them one common focus: the consumer. According to A.G. Lafley, focusing on innovation as a core strength throughout the company directly influenced P&G’s performance. The company’s commercial success rate grew from between 15% and 20% in 2000 (that is, for every six new products introduced, one would return the company’s investments) to between 50 & 60 % by 2008.
The organisation gradually became more customer-centric, and by 2015 it introduced an open-innovation strategy, also known as a Co-creation strategy. An open innovation strategy collates ideas from various stakeholders, including and especially the target market. Procter & Gamble introduced new strategies in 2015 to improve its position as a market leader and ensure it continues to abide by its innovative approach to market growth. Through the organisation’s customer-centric approach, the company focused on the brands where 90% of revenue and 95% of their profits were generated and proceeded to discontinue, consolidate, and divest over 59% of its existing products. This approach, although radical, was well informed by their application of their innovative strategy, which led to a better understanding of client needs and customers’ reactions to their products. By the first quarter of 2019, the organisation reported a 4% growth in net sales in 2021the CFO of P & G, Jon Moeller, stated that innovation contributed more than 35% to the organisation’s online market growth and a 50% increase in its e-commerce sales, which now contributes to 14% of its global sales revenue. According to the Wall Street Journal, the organisation also reported an approximately 7.2% increase in Year-on-Year revenue growth between 2020 and 2021.
Developing an innovation strategy is essential to deploying successful innovative products/services within an organisation such as Procter & Gamble; another vital step is driving these innovation strategies to implement and deploy innovation successfully.
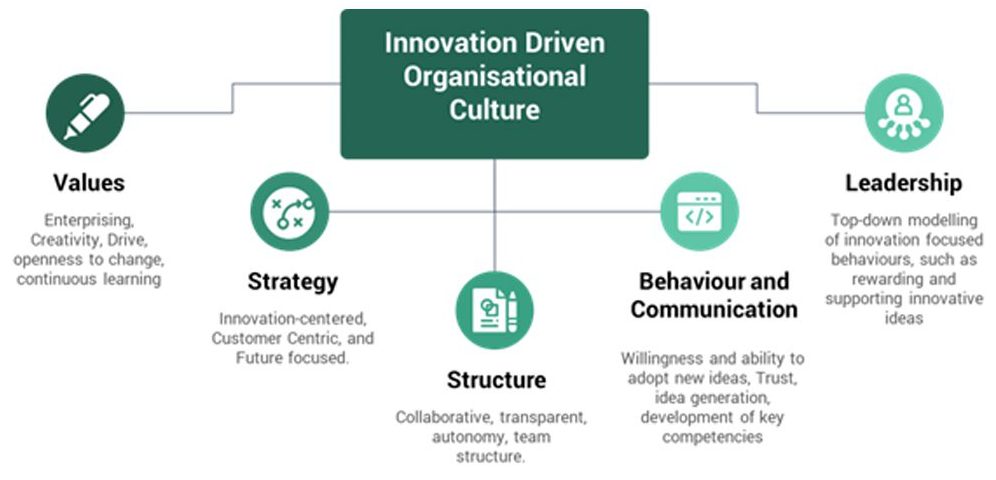
In the case of P&G, there were two key drivers of the successful implementation of their innovation strategy: organisational culture and change management. An organisation’s culture is the personality and identity; it is the foundation of true and impactful transformation. As depicted below, an organisational culture that drives innovation and change has five (5) structural elements.
All elements within an innovation-driven organisational structure are equally important; however, leadership is a crucial element that drives the culture. Leadership within an organisation should model the culture with which they would like to guide the organisation; as such, leaders who aim to operate an innovation-driven culture should promote innovative disruption, if applicable, creativity within the organisation, and a swift and impactful implementation of ideas.
The second key driver of innovation strategy is Change management. Change management as described in the pcl. article titled “Understanding the building blocks of change management” aims to execute a strategy for effecting change, controlling change, and helping people adapt to change. Innovation requires organisations to be responsive and adaptable to change, and change management entails the necessary tools for an effective transformation process.
pcl. ‘s Strategy and Operations Transformation unit supports organisations in developing and implementing effective innovation strategies while managing the impact of change and ensuring that organisational cultures are well aligned to drive innovation successfully. At pcl. we can support your organisation’s innovation journey by ensuring alignment of all necessary variables, from developing your strategy, realignment of your organisational culture, and implementing a project management office to guide your change management process.
Written by:

Wonu Salawu
Senior Analyst